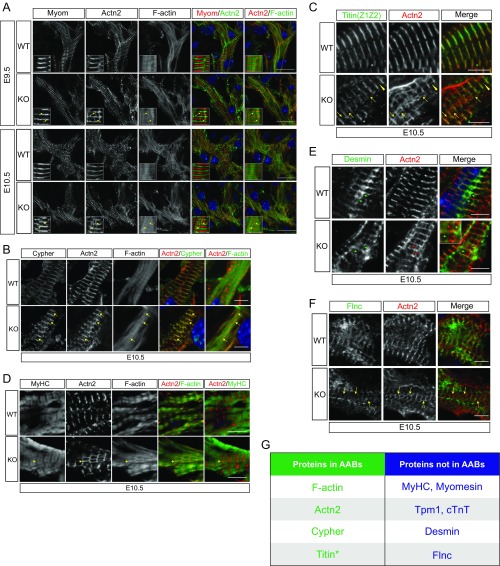
Fig. S3.
Characterization of AABs. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of WT and HSPB7 KO E9.5–E10.5 heart sections stained with antibodies against α-actinin (Actn2), phalloidin (F actin), and (A) myomesin (Myom), (B) Cypher, and (D) Myosin heavy chain (MyHC). The locations of AABs or their relative locations are indicated by yellow arrows. High magnification views are shown as Insets in corresponding images. Colors are depicted in merged images. DNA is stained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar: A, 10 μm; B and D, 5 μm.) (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of WT and HSPB7 KO E10.5 heart sections stained with antibodies against titin (Titin Z1Z2), Actn2, and phalloidin (F actin). Yellow arrowheads indicate AABs that contain titin; yellow arrows indicate AABs that do not contain titin. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (E) Representative immunofluorescence images of WT and HSPB7 KO E10.5 heart sections stained with antibodies against desmin and Actn2. Red arrows indicate AABs; green arrows indicate desmin-containing structures that interconnect Z lines. Inset shows an enlarged view of the region marked by the yellow box in the HSPB7 KO merged image. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (F) Representative immunofluorescence images of WT and HSPB7 KO E10.5 heart sections stained with antibodies against Flnc and Actn2. The locations of AABs or their relative locations are indicated by yellow arrows. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (G) A table summarizing the protein components of AABs as discovered from our immunofluorescent analyses. *In rare cases. (Magnification: A, Insets, 3.3×; E, Inset, 1.7×.)