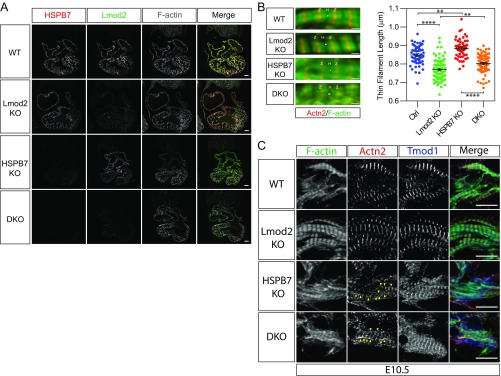
Fig. S5.
HSPB7 represses formation of AABs independent of Lmod2. (A) Immunofluorescence images of WT, Lmod2 KO, HSPB7 KO, and Lmod2/HSPB7 double KO (DKO) E10.5 heart sections stained with antibodies against HSPB7, Lmod2, and phalloidin (F actin). (Scale bar: 100 mm.) (B) Representative immunofluorescence images (Left) and thin filament length measurements (Right) of control (Ctrl; including WT and HSPB7 heterozygous KO), Lmod2 KO, HSPB7 KO, and Lmod2/HSPB7 DKO E10.5 embryos. Two embryos, 50–78 sarcomeres measured for each group. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Control, 0.849 ± 0.0069 mm; Lmod2 KO, 0.77 ± 0.0066 mm; HSPB7 KO, 0.885 ± 0.0074 mm; DKO, 0.802 ± 0.006 mm. Statistical significance was determined with one-way ANOVA. H, actin-free H zone; Z, Z lines. **P < 0.01 (Ctrl vs. HSPB7 KO, P = 0.0033; Lmod2 KO vs. DKO, P = 0.0021); ****P < 0.0001. (Scale bar: 1 μm.) (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of WT, Lmod2 KO (Lmod2 KO), HSPB7 KO, and Lmod2/HSPB7 DKO E10.5 heart cryosections stained with antibodies against Tmod1, α-actinin (Actn2), and phalloidin (F actin). AABs are indicated by yellow arrowheads. (Scale bar: 10 mm.)