Fig. 6.
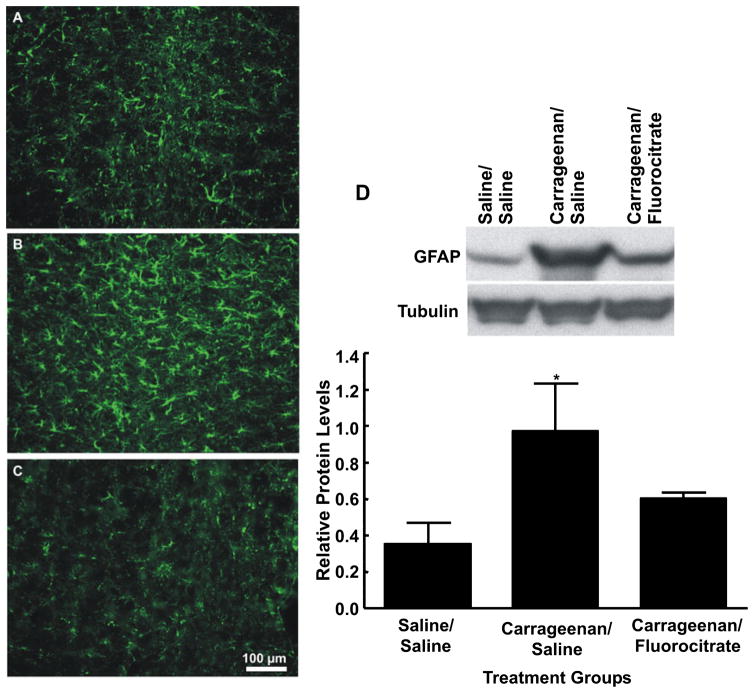
Medullary sections obtained from rats treated with hindpaw injections of saline (A) or subjected to carrageenan-induced inflammation and receiving microinjections of vehicle (B) or 1 μg of fluorocitrate (C) in the rostroventromedial medulla (RVM) were labeled with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) for immunofluorescent visualization of astrocytes. Microinjection of fluorocitrate into the RVM 3 h after hindpaw injection of carrageenan produced a reduction in immunofluorescence intensity for GFAP along with morphological changes suggesting reduced astrocyte activation. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) The top blot shows examples of the bands immunoreactive against anti-GFAP. The bottom blot shows the bands immunoreactive against anti-tubulin after stripping and reprobing of the same membrane. The bar graph shows the mean levels of GFAP normalized to tubulin. Carrageenan administration produced significantly increased protein levels of GFAP as compared with saline-treated animals. Protein levels of GFAP from animals treated with fluorocitrate in the RVM were not significantly different from those in saline-treated animals. *P < 0.05, relative to saline/saline.