Figure 1.
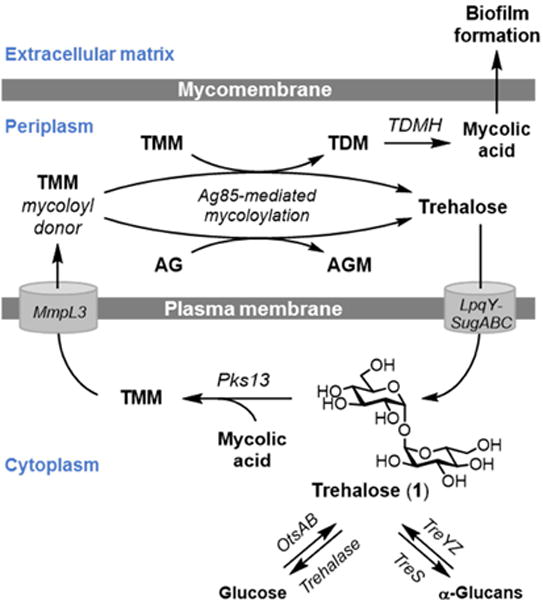
Trehalose (1) acts as a carrier of mycolic acids from the cytoplasm to the cell’s exterior, where mycolic acids are covalently attached to sugars to build the mycomembrane, or released in free form and incorporated into the biofilm extracellular matrix. Free extracellular trehalose generated through these processes is recycled back into the cell by the trehalose-specific transporter LpqY-SugABC. AG, arabinogalactan; AGM, arabinogalactan mycolate; TDM, trehalose dimycolate; TMM, trehalose monomycolate.
