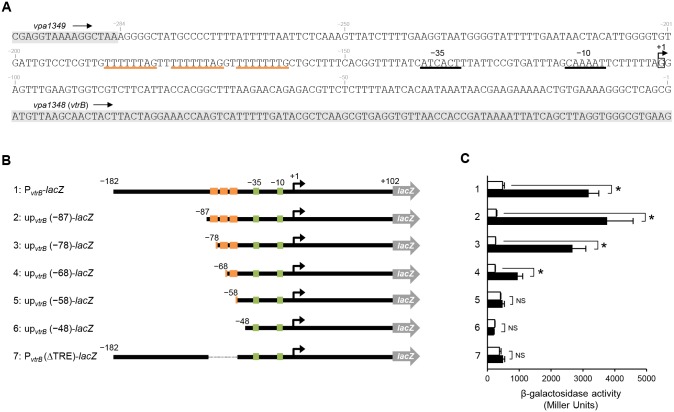
Fig 5. T-rich elements in the vtrB promoter region are required for transcriptional activation by VtrA.
(A) The nucleotide sequence of the vtrB promoter region. The transcriptional start site of the vtrB, determined by 5’-RACE, is indicated as +1. Putative −35 and −10 elements are underlined. Repetitive T-rich elements are underlined in orange. Gray shading indicates the regions of coding sequence of vpa1349 and vpa1348. (B) Schematics representing lacZ fusion reporters of the upstream promoter region of vtrB (PvtrB) and its truncated forms (upvtrB). Putative −35 and −10 promoter elements are shown in green. T-rich elements are indicated in orange. (C) β-galactosidase activity from PvtrB-lacZ and upvtrB-lacZ transcriptional reporters of V. parahaemolyticus ΔvtrA carrying an empty vector (white bar) or a VtrA expression plasmid (black bar). The values represent the mean ± SD for a minimum of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.01; NS, not significant, by Student’s t-test.