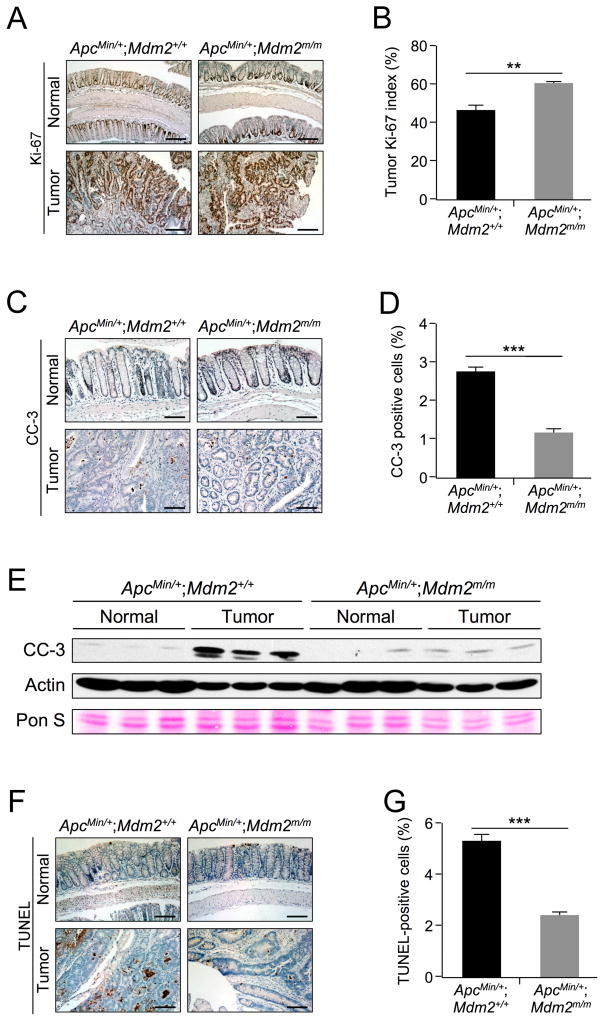
Figure 3. MDM2C305F mutation promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in APC loss-induced colon cancers.
A. Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining of proliferating cells in colon (Normal) and colonic adenoma (Tumor) tissue isolated from 15 week-old mice. In normal colon, the proliferating cells are located at the bottom of crypts, whereas tumor cells are highly proliferative. Scale bar = 200μm.
B. Percentage of Ki-67-positive cells in colonic adenomas was calculated quantitatively from five images using ImageJ. Error bars, ±SEM; **P<0.01.
C. Apoptosis was measured by IHC staining of cleaved caspase-3 (CC-3) in colon (Normal) and colonic adenoma (Tumor) tissue. Scale bar = 100μm.
D. Percentage of CC-3 positive cells in colonic adenomas was calculated quantitatively from five images using ImageJ. Error bars, ±SEM; ***P<0.001.
E. Western blotting was performed with protein lysates isolated from colonic polyps (Tumor) or adjacent normal colon tissues (Normal). n=3 for each group. Pon S = Ponceau S staining.
F. Apoptosis was measured by TUNEL staining in colon (Normal) and colonic adenoma (Tumor) tissue. In normal colon, apoptotic cells are located at the tips of the villi. Scale bar = 125μm.
G. Percentage of TUNEL positive cells from colonic adenomas was calculated quantitatively from five images using ImageJ. Error bars, ±SEM; ***P<0.001.