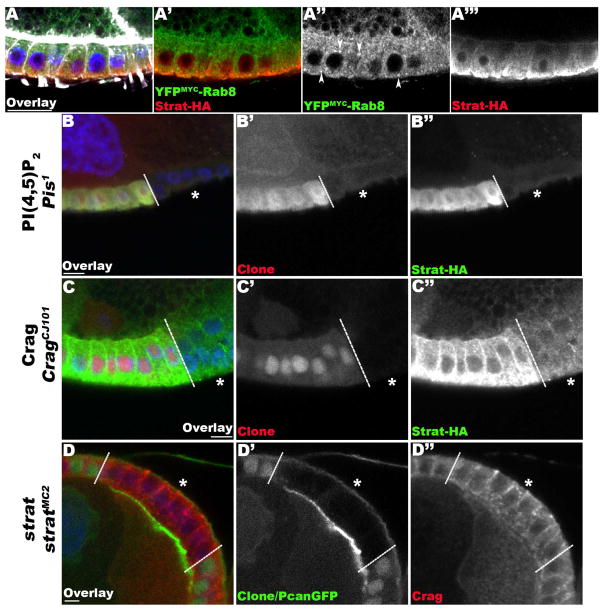
Figure 4. Stratum acts in a pathway dedicated to the basal restriction of BM proteins.
(A) Lg-section through egg chambers expressing YFPMYC-Rab8 (green) and Strat-HA (red), stained for F-Actin (white) and DNA (blue). Confocal Enhanced Resolution (ER) micrographs reveal that Rab8 has a diffuse cytoplasmic localization and accumulates in intracellular structures (arrowheads; A′, A″). Conversely, Strat-HA is basally distributed (A′, A‴). (B–C) Lg-section through the FE of an egg chamber containing Pis1 (B) and CragCJ101 (C) mutant clones, marked by the absence of intracellular RFP, expressing Strat-HA (green), and stained for DNA (blue). (D) Lg-section through the FE of an egg chamber containing a stratMC2 mutant clone, marked by the absence of intracellular GFP, expressing Pcan-GFP (green) and stained for DNA (blue). Dashed lines indicate clonal boundaries; asterisks (*) specify homozygous mutant FCs. In Pis and Crag mutant FCs, Strat-HA levels are overall reduced (B″, C″). However, the distribution of Crag is not significantly affected in strat mutant FCs (D″). Bars, 10 μm.