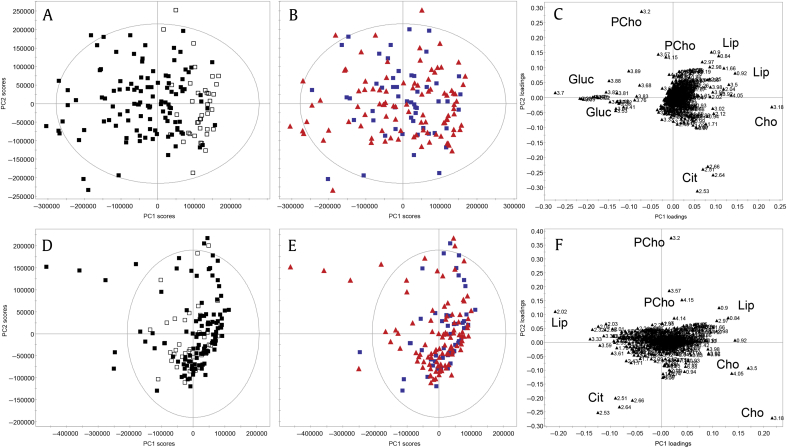
Fig. 2.
Principal components analysis of seminal plasma NMR spectra from men being investigated for prostate cancer (n = 151), prepared with different buffer solutions (Hanks Balanced Salt Solution: filled square, phosphate buffered saline: empty square). (A–C) Initial sample clustering is observed due to the difference in buffer solutions and resulting sample glucose content (principal component 1) and intersample differences in metabolite (citrate, choline, lipids/lipoproteins and phosphocholine) variation (principal component 2). (D–F) After add-to-subtract elimination of glucose, the previously observed effects of different buffer solutions are no longer apparent (D). No clustering was present according to CaP status (blue squares = benign; red triangles = CaP). (A, B, D, E) Scores plots. (C, F) Loadings plots. CaP, prostate cancer; Cho, choline; Cit, citrate; Gluc, glucose; Lip, lipids/lipoproteins ; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; PCho, phosphorylcholine; PC, principal component.