Fig. 1.
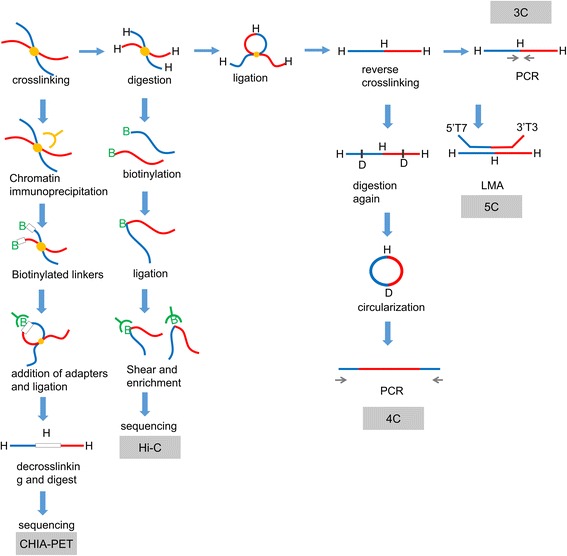
Overview of 3C-based C-techniques. After crosslinking, chromatin is digested into 4-10 kb pieces by restriction enzymes, followed by ligation and reverse crosslinking to change the crosses into lines. An additional digestion step is added in 4C. LMA is used instead of PCR, which is commonly used in 5C; biotinylation and streptavidin are used in Hi-C, and a chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP) step is added in ChIA-PET
