Fig. 6.
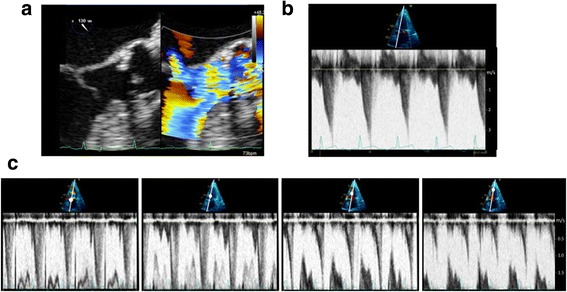
Left ventricular cavity obstruction. Obstruction of the left ventricular cavity can be due to anatomical factors and/or precipitated by LV cavity obstruction from hypovolaemia, excessive inotropic agents, predisposing anatomical abnormalities, etc., a systolic anterior motion of theanteiror mitral valve leafelet is frequently seen, often with resulting mitral regurgitation. Accurate imaging to determine location of the obstruction is required. b Continuous wave Doppler can identify an obstruction through recognition of the classic ‘dagger’ shaped curve with its peak in late systole. c Pulsed wave Doppler can identify the point of restriction by sequentially moving the gate from the left ventricle outflow tract to the apex looking for the point of maximal flow (note that aliasing is frequently seen where the maximum gradient is too high for the pulsed wave Doppler scale)
