Figure 16.
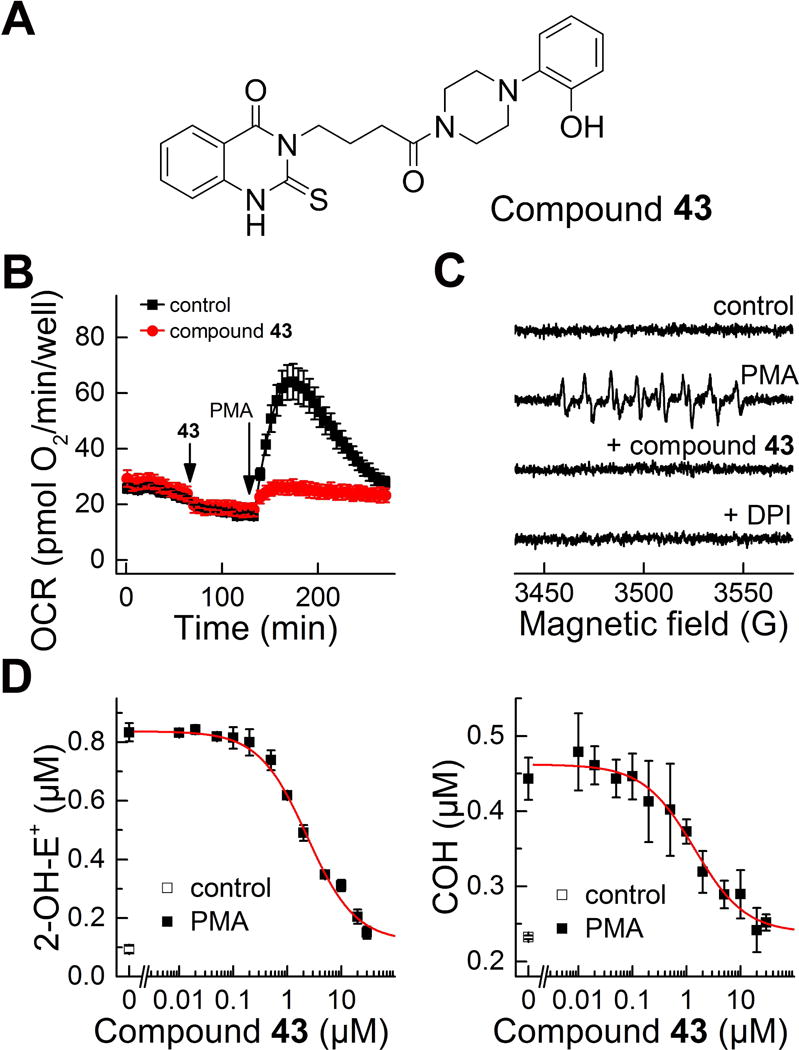
Confirmatory assays used for further characterization of the positive hits from HTS campaign. (A) Structure of the identified hit (compound 43 from ref. (79)). (B-C) Effect of the identified hit on the PMA-stimulated oxygen consumption rates (B) and formation of DEPMPO superoxide spin adduct (C). (D) Concentration dependence of the compound 43 on PMA-stimulated probe oxidation by dHL60 cells in the HPLC-based assays for simultaneous monitoring of O2•− and H2O2. (This research was originally published in Journal of Biological Chemistry. Zielonka, J., Cheng, G., Zielonka, M., Ganesh, T., Sun, A., Joseph, J., Michalski, R., O’Brien, W. J., Lambeth, J. D., & Kalyanaraman, B. High-throughput assays for superoxide and hydrogen peroxide: design of a screening workflow to identify inhibitors of NADPH oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2014; 289: 16176–16189. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.) (79)
