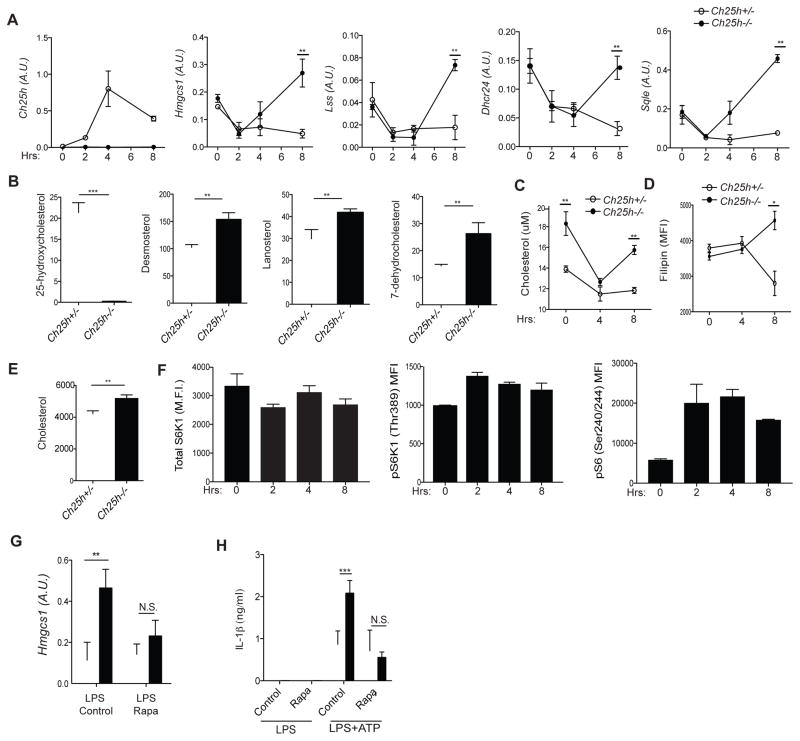
Figure 2. Ch25h induction prevents cholesterol buildup in macrophages by enforcing repression of mTORC1-dependent SREBP activity.
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of Ch25h, Hmgcs1, Lss, Dhcr24, and Sqle in Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs stimulated with LPS. Data are standardized by comparison to Hprt, and A.U. indicates arbitrary unit (means+/−SD from 4 independent experiments). (B) LC-MS quantification of 25-HC, desmosterol, lanosterol, and 7-dehydrocholestrol in Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs stimulated with LPS for 8 hr. Y-axis indicates ng/2×106 cells. Data from two independent experiments (mean+/−SD). (C) Quantification of cholesterol content by Amplex Red fluorescence in Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs stimulated with LPS. Data from 4 independent experiments (mean+/−SD). (D) FACS-based readout of cholesterol content by Filipin staining. Representative of three independent experiments (mean+/−SD). (E) GC-MS quantification of cholesterol content in Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs stimulated with LPS for 8 hr (n=3, mean+/−SD). (F) Flow cytometry for pS6K1 (Thr389) and pS6 (S240/244) from BMDMs stimulated with LPS. (G) RT-qPCR analysis of Hmgcs1 expression in Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs treated with LPS and DMSO or rapamycin. Data from three independent experiments (mean+/−SD). (H) IL-1β ELISA from supernatants of Ch25h+/− and Ch25h−/− BMDMs treated with LPS and DMSO or rapamycin, and then with ATP. Data from two independent experiments (mean+/−SD). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P < 0.005 (unpaired Students t test). See also Figure S1.