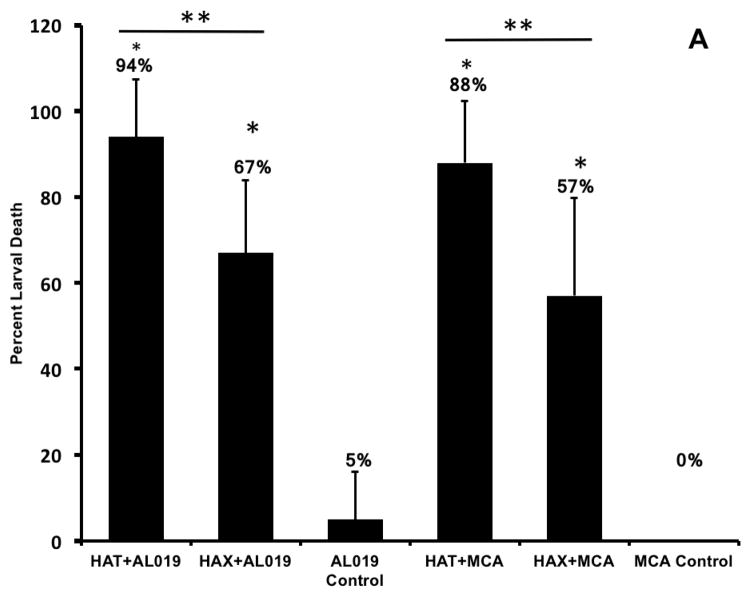
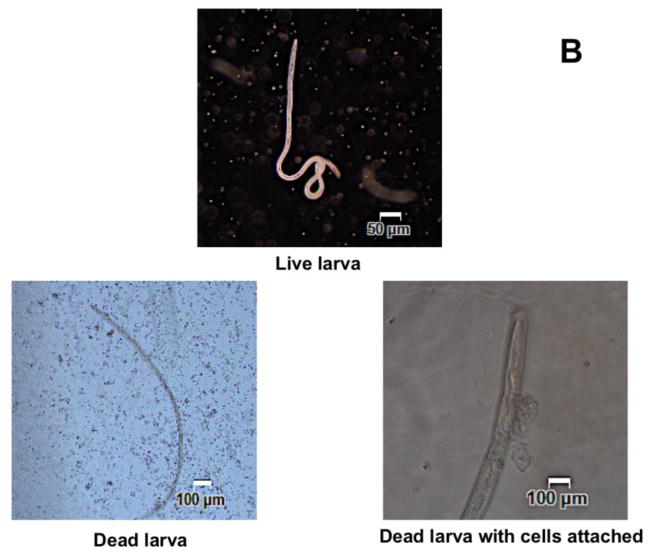
Figure 2. Percent protection in vaccinated animals was calculated by determining the percent larval death.
Figure 2A. Approximately 20 live B. malayi L3s sealed in a micropore chamber was surgically implanted into the peritoneal cavity of mice. 72 hrs after implanting the chambers were removed and the number of live and dead larvae was counted and percent larval death determined. Compared to the controls, there was significant larval death in vaccinated animals (Fig 2A). The highest percent of larval death (expressed as protection) was observed in mice immunized with rBmHAT. Comparison between rBmHAT and rBmHAX immunization plus AL019 adjuvant showed that significantly higher protection (p<0.0236) was observed in rBmHAT + AL019 immunized animals. Similarly, larval death in rBmHAT plus MCA immunized mice was significantly higher (p<0.0332) compared to those in rBmHAX plus MCA immunized mice. Figure 2B. Several cells were found attached to the dead larvae in the vaccinated animals (bottom panel). However, no cells were found attached to the live larvae collected from control animals. Magnification bars are indicated in each photomicrograph. n=10, statistically significant *p<0.0001 and **p<0.0006.