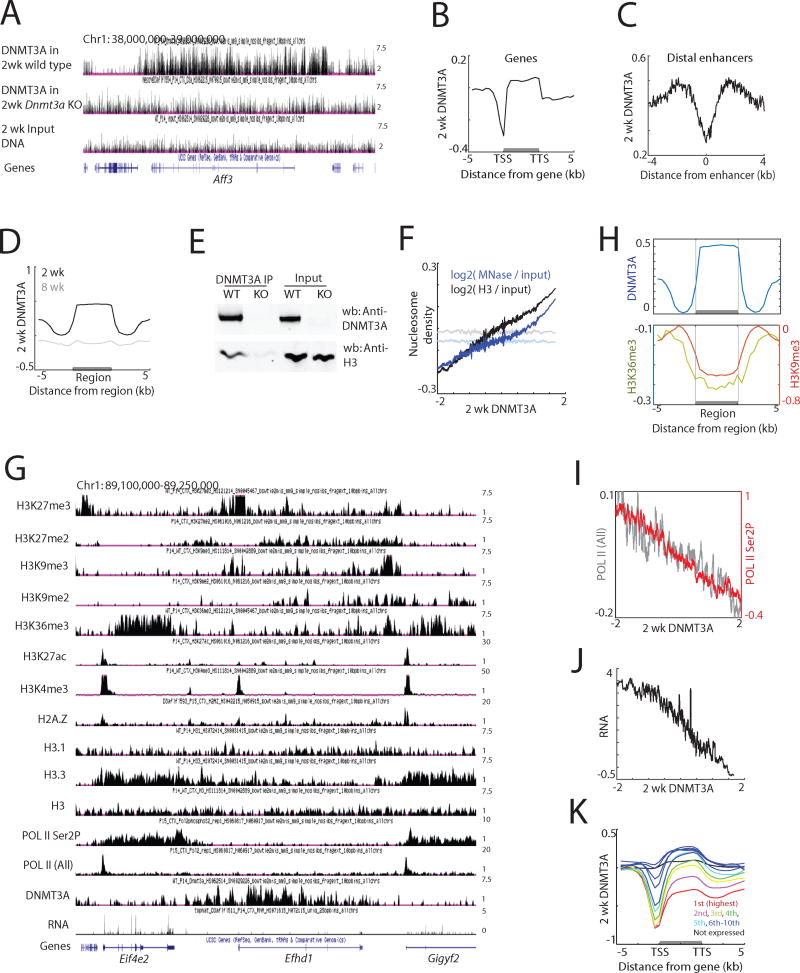
Figure 1. Genomic binding of DNMT3A in the brain during early life.
(A) Genome browser views of DNMT3A ChIP-seq data in wild type and Dnmt3a cKO cortex.
(B) Average DNMT3A distribution across all genes. DNMT3A signal was normalized to input DNA. TSS, transcription start site. TTS, transcription termination site.
(C) Average DNMT3A distribution across putative distal enhancers. H3K27ac data from the forebrain over multiple developmental points was used (Nord et al., 2013), and H3K27ac peaks more than one kilobase apart from annotated TSS were analyzed (N=38,620).
(D) Average distribution of 2-week and 8-week DNMT3A across DNMT3A-enriched regions in 2-week cortex (N=22,223).
(E) Immunoprecipitation of DNMT3A under non-denaturing conditions from 2-week cortical extracts from wild type and Dnmt3a cKO (KO) mice.
(F) DNMT3A binding and nucleosome density in two-week cortex across the genome in 5 kilobase tiles. Both MNase-seq and H3 ChIP-seq reads were normalized to sonicated input DNA (log2 ratio). The average nucleosome density was binned according to DNMT3A enrichment relative to input DNA. Nucleosome densities after random grouping of genomic tiles are shown as controls in faded lines (P<0.001, permutation test).
(G) Genome browser view of ChIP-seq data in the two-week cortex.
(H) Average distribution of H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 across defined DNMT3A-enriched regions.
(I) Correlation between DNMT3A binding and RNA POL II occupancy across gene bodies in the two-week cortex. The average POL II (all) or POL II (Ser2P) across gene bodies were binned according to DNMT3A density. Promoter regions were excluded from the analyses.
(J) Correlation between DNMT3A binding and gene expression in the two-week cortex. The average gene expression level was binned according to DNMT3A density.
(K) Average DNMT3A distribution over genes of different expression levels in the wild type cortex.
See also Figure S1.