Figure 1.
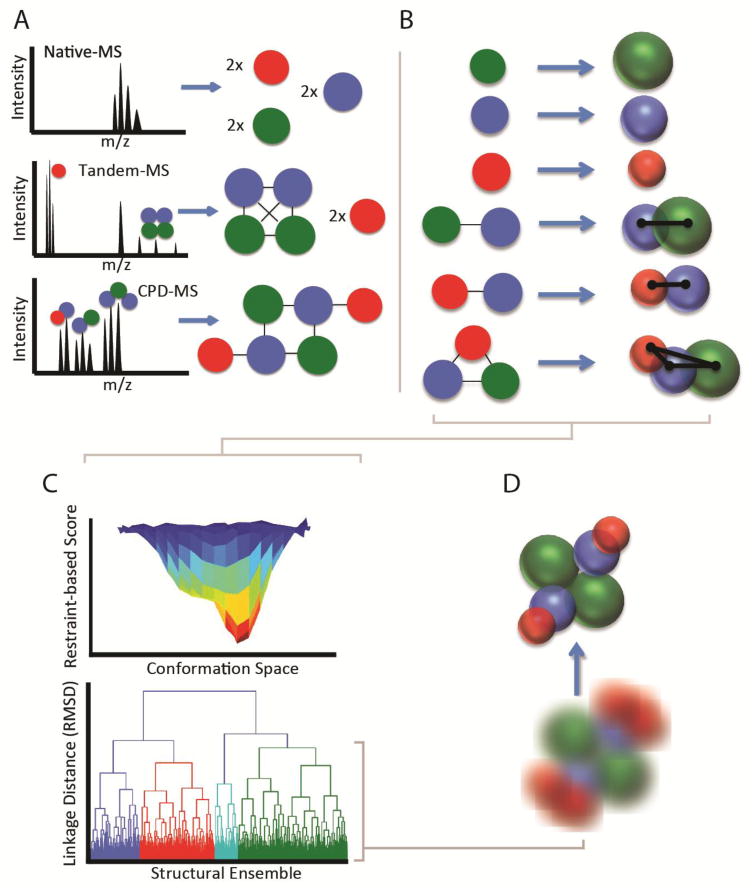
A general workflow for IM-MS-based modeling. A) native-MS, tandem-MS, and solution-phase disruption-MS yield increasing amounts of composition and connectivity information for a multiprotein complex. This information can be encoded with varying levels of ambiguity based on the information available. B) IM-MS data can be included to build a 3D topology mode. Individual subunits or domains can be encoded as spheres with radius derived from their measured CCS, while exact distances between subunits can be derived from CCS measurements of dimeric and trimeric species. C) Optimization of the experimentally-defined scoring function using a Monte Carlo method provides unbiased sampling of potential structures for high-stoichiometry complexes. These structures form an ensemble which is subjected to clustering analysis to mine for predominant structural families D) Structural families detected by clustering can be characterized in aggregate using kernel density functions, mean structures and standard deviations, or individual structures can be identified as representative of the family.
