Table 1.
Summary of the photophysical and redox properties of the photosensitizers used to activate P450 enzymes as well as their respective structures.
| Light-harvesting unit |
Structure | Absorption and Emission max |
Reduction potentiala |
Electron supplierb |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||
| 3-nm CdS-Quantum Dots Capped with mercaptoacetic acid |
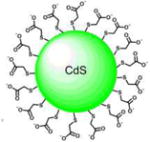
|
λmax(Abs) = 390 nm | 3 eV bandgap | H2O | [34] |
| λmax(Em) = 550 nm | |||||
|
| |||||
| 3,10- dimethyl-5-deazaflavin |
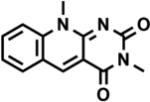
|
λmax(Abs) = 390 nm | −0.770 V | EDTA | [35] |
| λmax(Em) = 480 nm | |||||
|
| |||||
| Photosystem I |
|
λmax(Abs) = 700 nm | −1.2 V | Plastocyanin | [36] |
|
| |||||
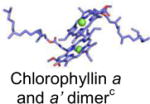
| FAD, FMN, RBFd |
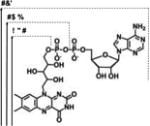
|
λmax(Abs) = 441-43 nm | −0.240 V | EDTA | [35] |
| λmax(Em) = 530-32 nm | |||||
|
| |||||
| Eosin Y |
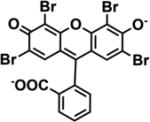
|
λmax(Abs) = 525 nm | −1.16 V | TEOA | [24] |
| λmax(Em) = 543 nm | |||||
|
| |||||
| Ruthenium diimine |
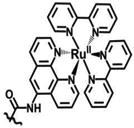
|
λmax(Abs) = 452 nm | −1.28 V | DTC | [37] |
| λmax(Em) = 620 nm | |||||
eported vs NHE
EDTA: ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, TEOA: triethanolamine; DTC: diethyldithiocarbamate
Mg2+: green sphere
FAD: Flavin adenine dinucleotide; FMN: Flavin mononucleotide; RBF: Riboflavin.
