Fig. 2.
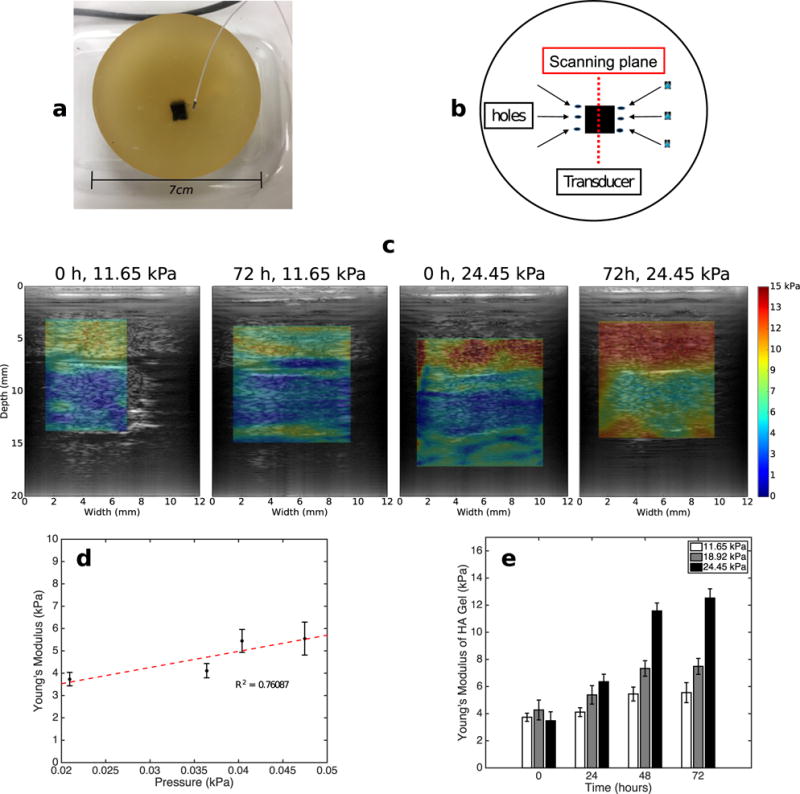
(a) Phantom containing cross-linked hyaluronic acid (HA) inclusion embedded in gelatin. We used the probe illustrated in (a) to measure interstitial fluid pressure in the HA inclusion. (b) Schematics of the phantom, ultrasound transducer and hole used to increase permeability. (c) Modulus elastograms obtained from phantoms that we submerged in phosphate-buffered saline for 0 and 72 h. The Young’s moduli of the gel surrounding the phantoms were 11.65 and 24.45 kPa. (d) Young’s modulus versus pressure within the HA inclusion that we embedded in a gel with Young’s modulus of 11.65 kPa. (e) Bar plot of Young’s moduli of the HA gels for the 11.65-, 18.92- and 24.45-kPa phantoms as a function of time.
