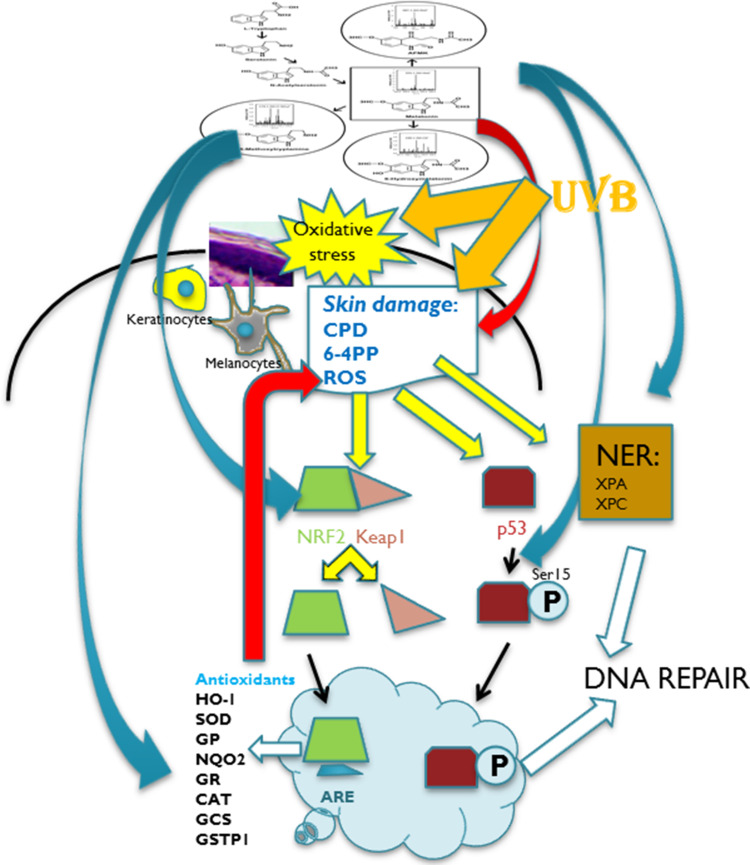
Fig. 3.
Melatonin and its metabolites act as radioprotectors on epidermal keratinocytes and melanocytes. Local melatoninergic system in skin includes sequential transformation of tryptophan to serotonin and melatonin. NAS is both precursor and metabolite of melatonin. Through indolic pathways, melatonin is hydroxylated to 6(OH)M or metabolized to 5-MT. Through kynuric pathway, melatonin is transformed to AFMK. UVB is absorbed in the epidermis inducing oxidative stress and direct DNA damage. Melatonin and its metabolites inhibit oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by UVB (red arrow). In response to oxidative stress, NRF2 is released from Keap (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein) and translocated to the nucleus. This process is stimulated by melatonin and its metabolites (blue arrow). NRF2 binds to ARE (anti-oxidant response element) and further activates detoxifying enzymes and proteins: melatonin and its metabolites also stimulate the production of anti-oxidants (blue arrow) which further reduces UVB-induced damage to melanocytes and keratinocytes (red arrow). UVB-induced DNA damage to the skin promotes p53 expression, which after phosphorylation accumulates in the nucleus and activates the DNA repair process. Melatonin and its metabolites stimulate phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 (blue arrow). Melatonin and its metabolites induce repair of DNA damaged by UVB by enhancing the NER core factors: complementation group C (XPC) and complementation group A (XPA)-DNA interactions (blue arrow). HO-1 heme oxygenase 1, SOD superoxide dismutase, GP glutathione peroxidase, NQO2 quinone reductase 2, GR glutathione reductase, CAT catalase, GCS glutamylcysteine synthetase, GSTP1 glutathione-S-transferase