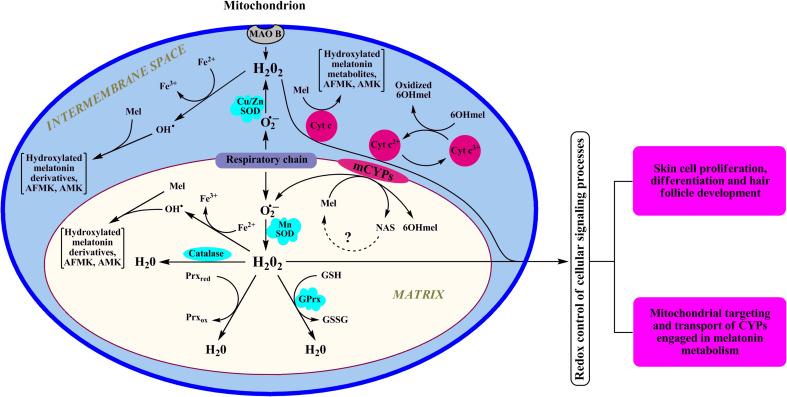
Fig. 4.
Dynamic interaction between melatonin, melatonin metabolites, and mitochondrion redox homeostasis. In mitochondria, cytochrome c is a natural scavenger of H2O2 preventing its accumulation via mechanism linked to reverse electron transfer from succinate to NAD+ [88] or through “alternative electron leak pathway” [89]. The latter mechanism that requires ferrocytochrome is active under physiological conditions. However, if there is a block in electron transfer, ferricytochrome cannot be reduced and cytochrome c would lose its capability to scavenge H2O2. Reduction of ferricytochrome c by 6-hydroxymelatonin (6OHMel) allows use of the electrons removed from the 6-hydroxymelatonin for the detoxication of H2O2. In addition, when electron transport is disrupted, cytochrome c-dependent pseudoperoxidase reaction with melatonin could become dominant [62]. GPrx glutathione peroxidase, Prx peroxiredoxin, Mel melatonin, 6OHmel 6-hydroxymelatonin, MAO B monoamine oxidase B, SOD superoxide dismutase