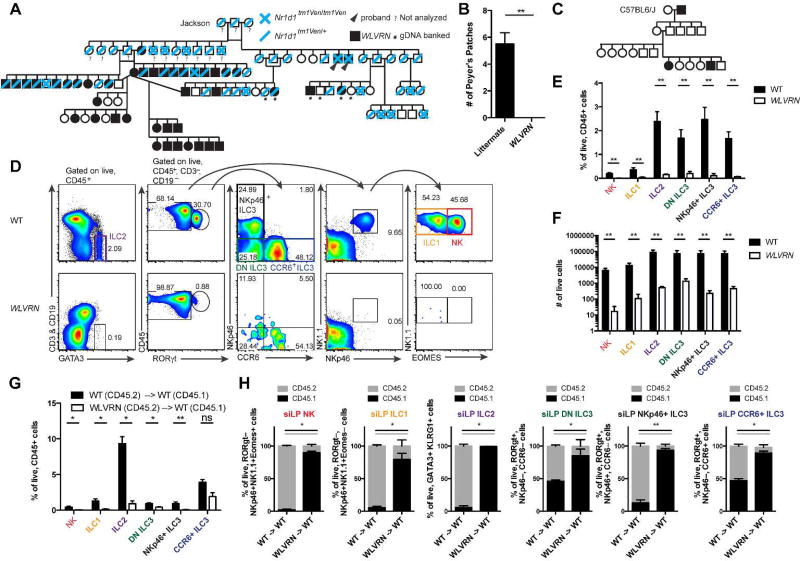
Figure 1. ILCs fail to develop in WLVRN mice.
(A) Pedigree analysis of intercrossed heterozygous B6.Cg-Nr1d1tm1Ven/LazJ mice beginning with original breeding trio purchased from Jackson Laboratories. WLVRN probands emerge in F1. (B) Number of PPs in WLVRN mice compared to littermate controls. (C) Pedigree analysis of an Nr1d1+/+ WLVRN mouse backcrossed to C57BL6/J. (D–F) Evaluation of ILC populations from the siLP of Nr1d1+/+ WLVRN or unrelated WT control mice. (D) Gating strategy and representative flow plots. (E) Frequency and (F) total number of ILC subsets. (G–H) CD45.2 WT or WLVRN donors were transplanted into CD45.1 WT lethally irradiated recipients. (G) Frequency of recovered siLP ILCs from bone marrow chimeras and (H) the degree of chimerism per subset 8 weeks post-irradiation.. (B, D–H) Data represent (B, D–F) n=5 mice per group or (G–H) n=4–5 mice per group from 2–3 independent experiments. *p<.05, ** p<.01, two-tailed Mann-Whitley test.