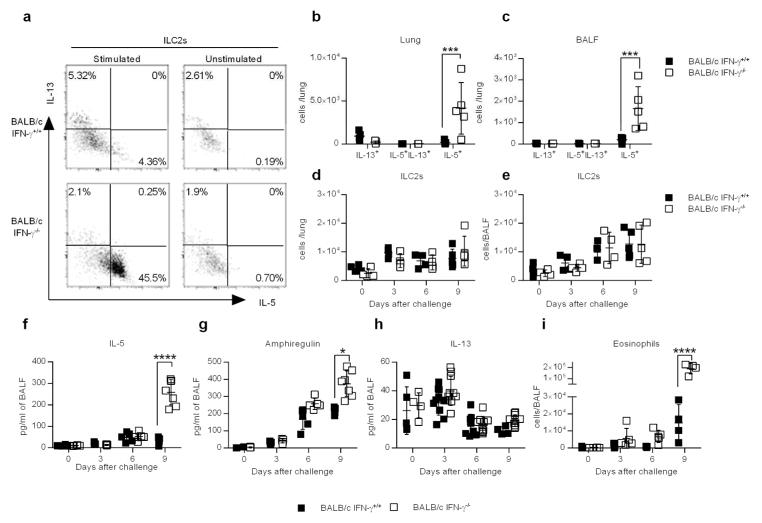
Figure 3.
IFN-γ suppresses ILC2 function during CA04 infection. (a) Representative dot plots showing percentages of ILC2s (CD90+Lin-CD127+KLRG1+ST2+) that were positive for IL-13 or IL-5. Cells were harvested 9 days after CA04 virus infection and restimulated ex vivo with PMA (50ng/ml) and ionomycin (500ng/ml) in the presence of Brefeldin A (10 μg/ml). Unstimulated cells were used as a negative control. (b,c) Total number of cytokine-secreting ILC2s in the lungs (b) and BALF (c) 9 days after CA04 infection. (d,e) Total number of ILC2s in the lung (d) and BALF (e) (f–h) Levels of IL-5 (f), Amphiregulin (g), and IL-13 (h) in the BALF of mice infected with 2000 PFU of CA04 virus. Data shown were pooled two independent experiments. (i) Total number of SiglecF+CD11b+Ly6G-CD11c- eosinophil numbers in the BALF of mice infected with 2000 PFU of CA04 virus. Data shown were pooled two independent experiments. (b–i) Statistical analyses were performed by two-way ANOVA. * P<0.05; *** P<0.001; **** P<0.0001.