Fig. 1.
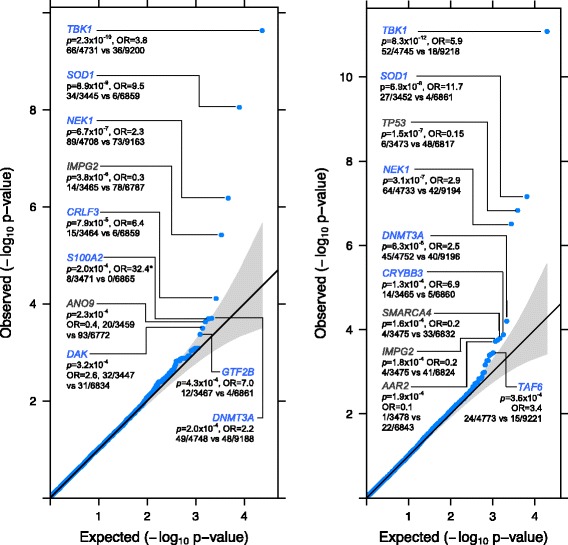
Quantile–quantile plots of the analysis of rare variant counts in combined Chinese and European data (up to 4797 cases and 9236 controls). The Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test was applied to qualifying variants under three models: (L) dominant coding; (R) dominant not benign; and dominant LOF (Additional file 2: Figure S1). Test statistics are provided for the genes with the top ten associations (blue = increased risk, grey = reduced risk; *no qualifying variants were observed in controls for gene S100A2, so the OR was estimated by adding 0.5 to each cell of the largest cohort). The Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold was p ≤ 1.9 × 10–6, based on 26,214 tests across 18,117 genes. The genomic inflation factor, lambda (λ), was 1.069 for the dominant coding analysis and 1.067 for the dominant not benign analysisrecognised in our Chinese sample
