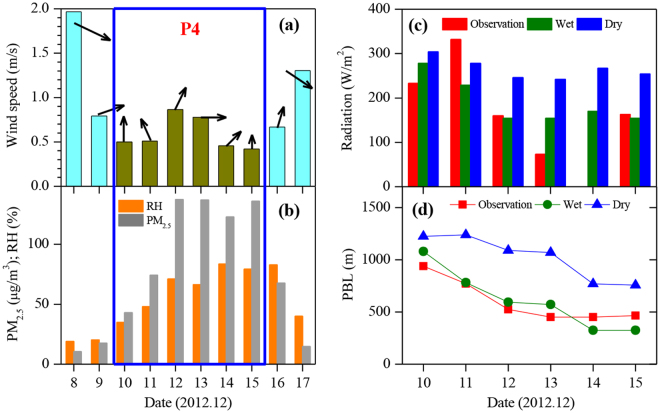
Figure 2.
A case study of the effects of water vapour on solar radiation, PBL heights, and PM2.5 concentrations. (a) shows the measured wind speeds (m s−1) prior to P4, during P4 and after P4. (b) shows the measured PM2.5 concentrations (μg m−3) and RH (%) prior to P4, during P4 and after P4. (c) shows the measured and modeled (“dry” and “wet” cases) surface solar radiation during P4. (d) shows the measured and modeled (“dry” and “wet” cases) PBL heights. The results suggest that water vapour plays an important role in the reduction of solar radiation and PBL heights.