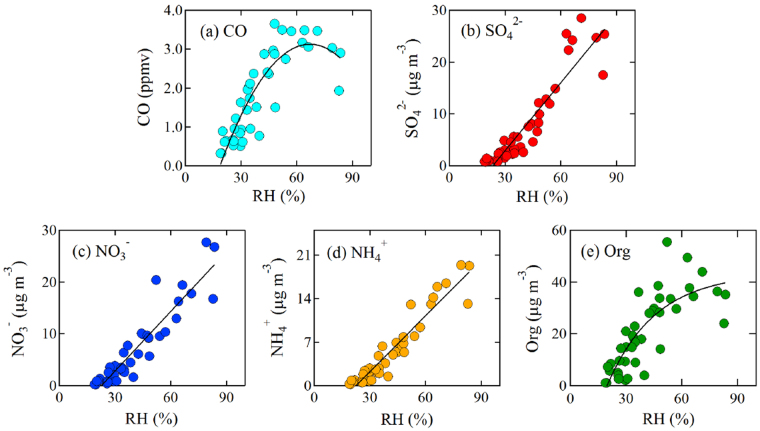
Figure 4.
The variability of measured CO and aerosol composition (SO4 2−, NO3 −, NH4 +, Organics) under different RH conditions during 2012–2013 winter time in Beijing. As RH increased to a critical value (50%), the CO, which can be considered as an inactive-chemical tracer, remained at a relatively constant value. The secondary aerosols (NO3 −, SO4 2−, NH4 +), however, showed a rapid increase with the increase in RH values. The organic aerosol (Org) contained both secondary and primary component, resulting in a mixed behaviour between the CO and secondary aerosols.