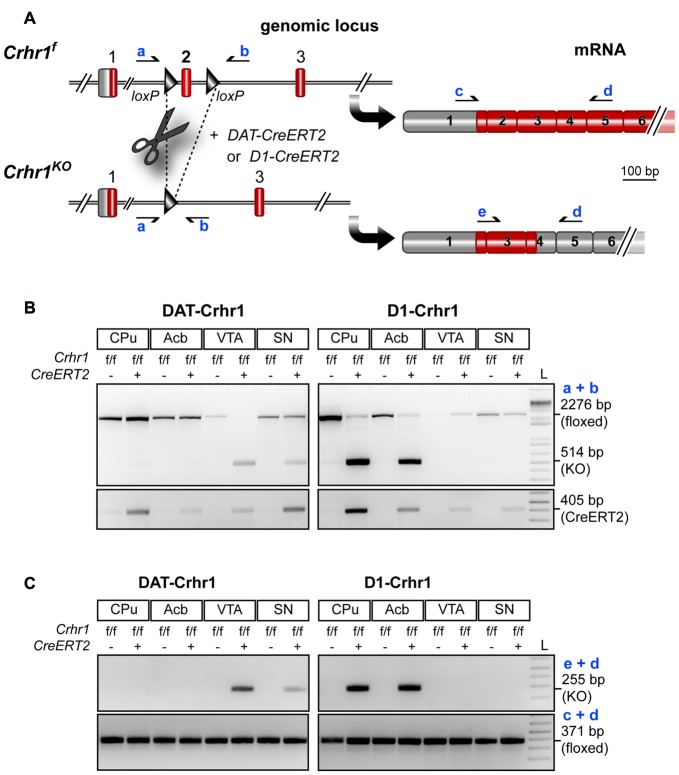
Figure 2.
Conditional inactivation of Crhr1 in dopamine transporter (DAT)-Crhr1 and D1-Crhr1 mice. (A) Schematic illustration of conditional Crhr1 allele (Crhr1f) in which the critical exon 2 is flanked by loxP sites and corresponding mRNA transcripts. Cre recombinase-mediated deletion of exon 2 results in functional inactivation of Crhr1 (Crhr1KO) due to a premature stop codon in exon 4 Primers (a) and (b) for detection of the recombination event on genomic level as well as primers (c), (d) and (e) for detection of the mutant transcript are depicted. (B) Brain region-specific detection of Crhr1 inactivation on the genomic level in dopaminergic neurons in the VTA and substantia nigra (SN) of DAT-Crhr1 mice as well as in dopaminoceptive neurons in the caudate putamen (CPu) and nucleus accumbens (Acb) of D1-Crhr1 mice. The floxed exon 2 and thus intact Crhr1 is detected by a 2276 bp PCR product. Deletion of exon 2 and concomitant inactivation of Crhr1 is detected by a 514 bp PCR product. Conditional Crhr1 inactivation is based on the presence of tamoxifen-inducible CreERT2 detected by a 405 bp PCR product. (C) Brain region-specific detection of the mutant Crhr1 transcript lacking exon 2 in the VTA and SN of DAT-Crhr1 and CPu and Acb of D1-Crhr1 mice. The Crh1 transcript lacking exon 2 is detected by a 255 bp PCR product. As a control the wild-type transcript was detected in all brain regions analyzed in DAT-Crhr1 and D1-Crhr1 mice. Wild-type Crhr1 transcripts present in regions of Crhr1 deletion originate from Crhr1 expressed in non-dopaminergic or non-dopaminoceptive cells, respectively. Translated exons are depicted in red. 5′UTR and untranslated exons are depicted in gray.