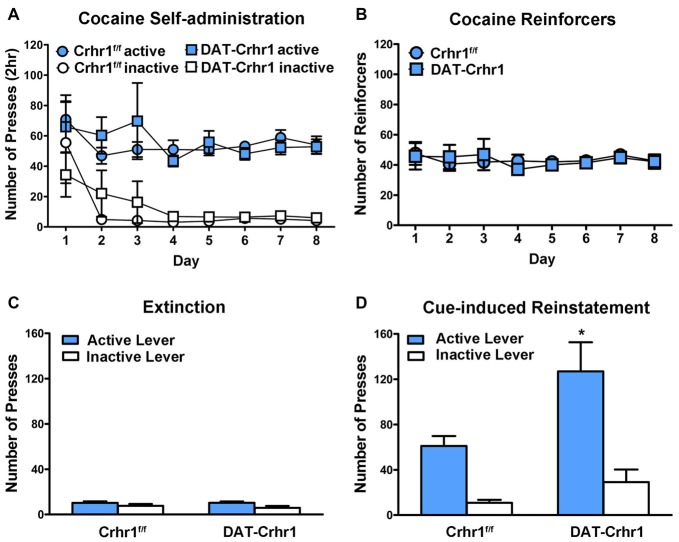
Figure 4.
Cocaine self-administration in DAT-Crhr1 and littermate Crhr1f/f control mice. (A) Both DAT-Crhr1 and controls demonstrated similar acquisition of the task, as demonstrated by a significant difference between responding on the active and inactive levers. Data represent mean number of presses (±SEM) on the active and inactive levers during eight daily 2 h sessions of cocaine self-administration (0.50 mg/kg/infusion). (B) There was no difference in DAT-Crhr1 mice and controls in the number of cocaine reinforcers achieved. Data represent mean number of cocaine reinforcers (±SEM) achieved during eight daily 2 h sessions of cocaine self-administration (0.50 mg/kg/infusion). (C) There was no difference in responding in DAT-Crhr1 mice and controls during the final 2 days of extinction trials. Data represent mean number of presses (±SEM) on the active and inactive levers during the final 2 days of daily 2 h extinction sessions. (D) DAT-Crhr1 mice demonstrated increased cue-induced reinstatement relative to controls, as indicated by an increase in responding on the active lever without a corresponding change in responding on the inactive lever. Data represent mean number of presses (±SEM) on the active and inactive levers during a single 2 h session of cue reinstatement. *p < 0.025 relative to active lever presses of control mice.