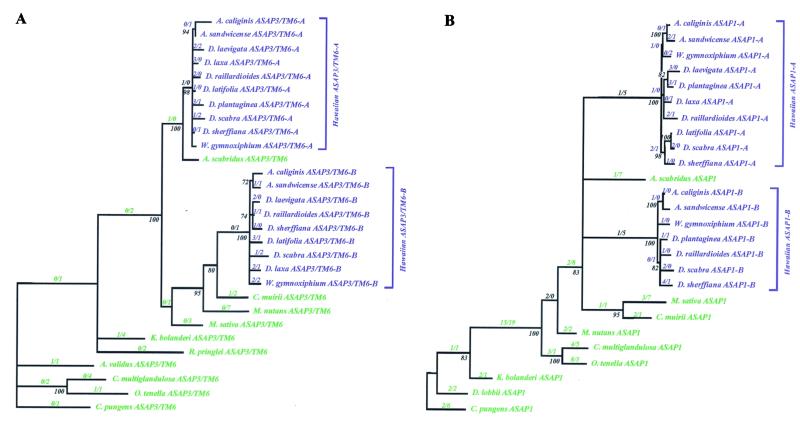
Figure 3.
Phylogenies of the (A) ASAP3/TM6 and (B) ASAP1 genes in the North American tarweeds (green) and Hawaiian silversword alliance (blue). The phylogenies were reconstructed by using coding region and noncoding region sequences. The numbers of nonsynonymous (N) and synonymous (S) nucleotide substitutions in the coding regions inferred along each branch by maximum likelihood ancestral state reconstructions are given as a ratio (N/S). Levels of bootstrap support are shown next to the nodes. Nodes with less than 70% bootstrap support, and with no coding region nucleotide substitutions inferred along the subtending branch, are collapsed. For the North American species, the generic abbreviations are: A, Anisocarpus; Ad, Adenothamnus; C, Carlquistia; Ca, Calycadenia; Ce, Centromadia; D, Deinandra; H, Harmonia; K, Kyhosia; M, Madia; O, Osmadenia; and R, Raillardella. For the Hawaiian species, the generic abbreviations are: A, Argyroxiphium; D, Dubautia; and W, Wilkesia.