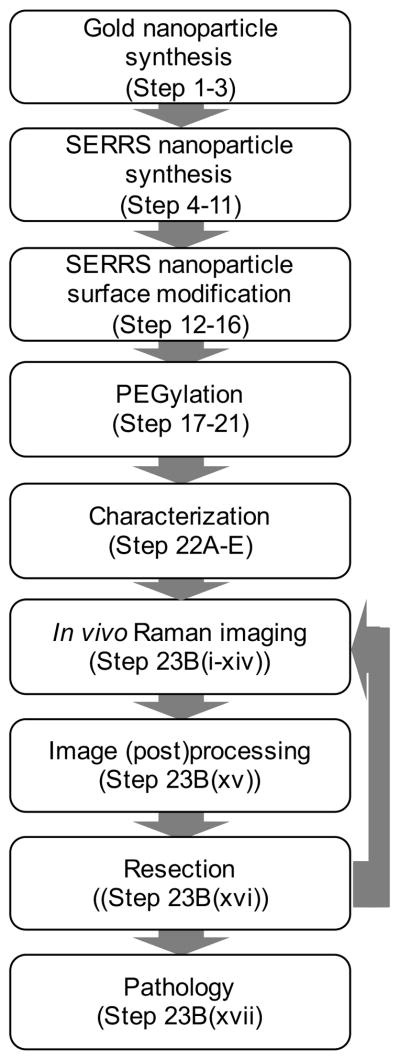
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the workflow for SERRS-based Raman imaging of cancer. Firstly, the gold nanocores are synthesized and coated with silica in the presence of a dye that is resonant with the excitation laser wavelength (i.e. 785 nm) to afford the SERRS nanoparticles. The surface of SERRS nanoparticles can be modified to include PEG functionality. The functionalized SERRS nanoparticles are injected intravenously via tail vein in tumor-bearing animals and imaged using Raman imaging. The data is converted into an image and enables SERRS-based image-guided resection. Rescanning of the tumor-bed ensure adequate resection. If residual SERRS signal is detected more tissue can be resected. Finally, the resected tissues are processed for histological examination.