Figure 3.
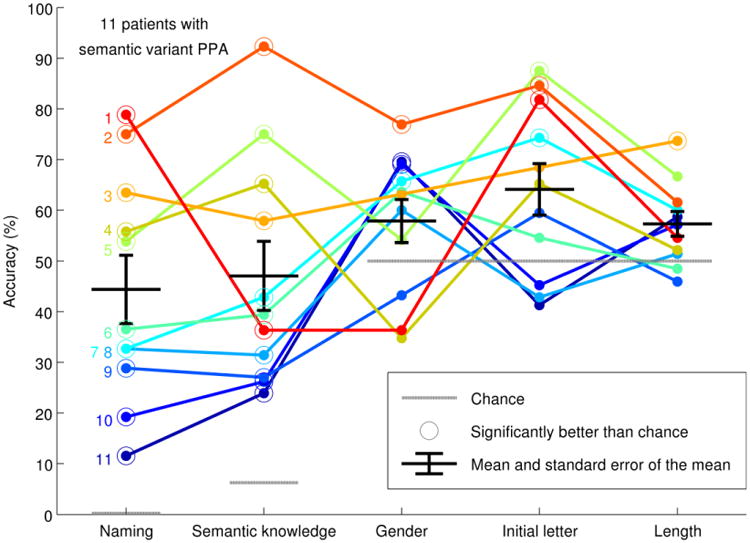
Access to different aspects of lexical items. For each of the 11 patients whose naming accuracy was < 80%, the accuracies for naming, conceptual knowledge, gender, initial letter, and length tasks are shown. The chance levels for each task are indicated with gray dotted lines, and individual scores that significantly exceed chance (p < 0.05) are circled. The mean and standard error of the mean are indicated with black lines and error bars.
