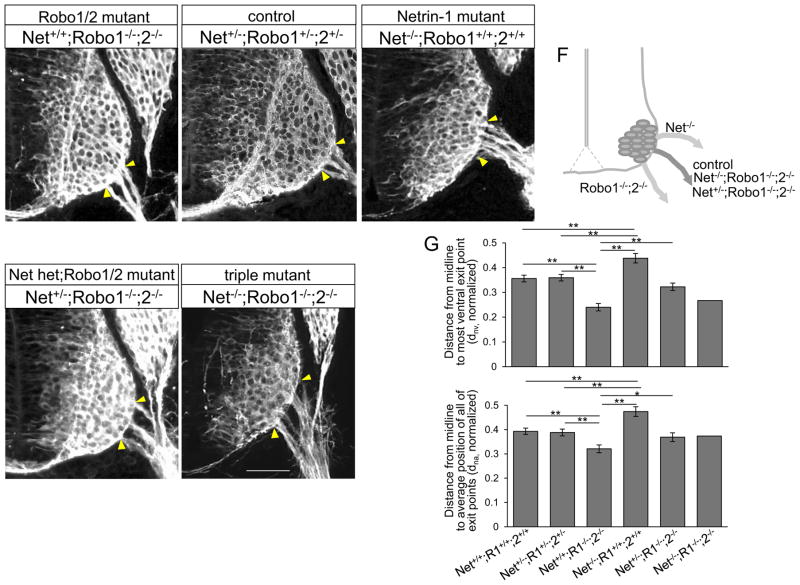
Figure 10. Motor exit points are positioned by a balance of Slit/Robo repulsion and Netrin-1/DCC attraction.
(A–E) βIII-tubulin labeling on Netrin-1/Robo1/2 combined mutant spinal cord sections of Netrin-1+/+;Robo1−/−;2−/− (Robo1/2 double mutant), Netrin-1−/−; Robo1+/+;2+/+ (Netrin-1 mutant), Netrin-1+/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− (Netrin-1 het; Robo1/2 double mutant) and Netrin-1−/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− (triple mutant) and their littermate controls, Netrin-1+/−;Robo1+/−;2+/− showing Netrin-1/Robo1/2 triple mutant has exit points at intermediate positions, similar to its littermate controls. (F) Schematic of locations of motor exit point in control and Netrin-1/Robo1/2 combined mutants. (G) Summary graphs show the distance from the midline to the most ventral exit point, and the distance from the midline to the average position of all of the exiting motor axon bundles in Netrin-1/Robo1/2 combined mutants, Netrin-1+/+;Robo1−/−;2−/− (n=6 embryos), Netrin-1−/−; Robo1+/+;2+/+ (n=6 embryos), Netrin-1−/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− (n=1 embryo) and Netrin-1+/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− (n=10 embryos) compared to their littermate controls, Netrin-1+/−;Robo1+/−;2+/− and wildtypes (n=6 embryos, respectively). The distances in Netrin-1−/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− and Netrin-1+/−;Robo1−/−;2−/− are not significantly different from their littermate controls. Yellow arrow heads show the closest and farthest exit points from the ventral midline. Scale bars: A–E, 50 μm. *= P<0.01, ** = P < 0.001.