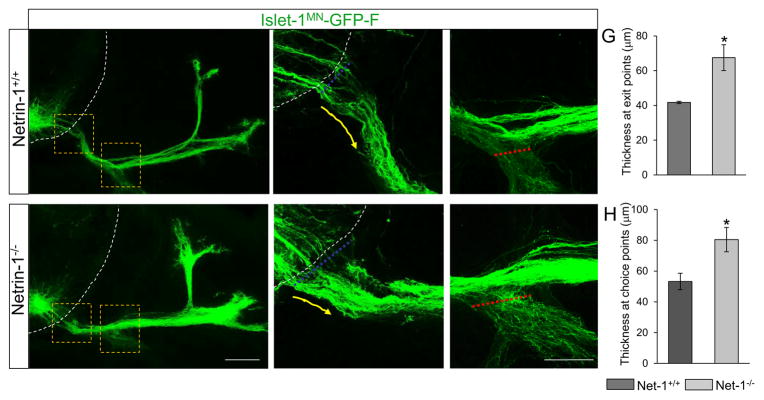
Figure 7. Spinal motor nerve projections are abnormal in Netrin-1 mutants.
(A–F) Spinal cord sections of Netrin-1+/+::Islet-1MN-GFP-F and Netrin-1−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F embryos (n=6 embryos for each genotype of E12.5; note that these examples appear slightly less advanced than in Fig 4) show that motor trajectories are widely dispersed at the exit points and at the choice points in Netrin-1−/−::Islet-1MN-GFP-F embryos. Dotted white lines in A, B, D, and E show the spinal cord. Yellow arrows in B and E show motor axon trajectories at exit points. (G) Quantification of the thickness at exit points (dotted blue lines in B and E) shows that Netrin-1 mutants have defasciculated exit points compared to their controls. (H) Quantification of the thickness at choice points (dotted red lines in C and F) shows enhanced defasciculation within the choice point, leading to extensive ventral ramus in Netrin-1 mutants. Scale bars: A, D, 100 μm; B, C, E, F, 50 μm. SC, spinal cord; DM, dermomyotome. *=P < 0.05.