FIGURE 4.
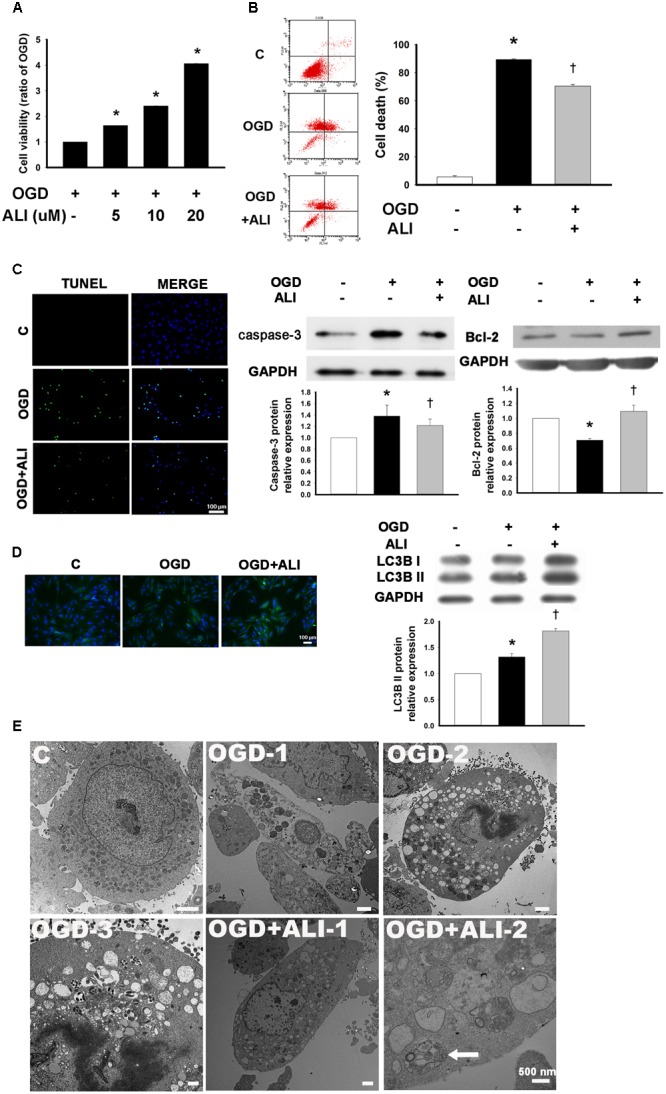
Aliskiren increases cell viability in oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD)-treated H9c2 cells via the upregulation of autophagosome formation. (A) Cardiomyocytes treated with 5, 10, or 20 μM of aliskiren were exposed to OGD for 16 h, and then cell viability was examined by the MTT assay. ∗P < 0.05 compared with OGD. (B,C) Cardiomyocytes treated with 20 μM aliskiren were exposed to OGD for 16 h. Cell death was evaluated with Annexin V/PI staining by flow cytometer and TUNEL staining (Bar: 100 μm), and the protein expression of caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in OGD-treated H9c2 cells was assessed by Western blotting. (D) Effect of aliskiren on LC3B expression in OGD-treated H9c2 cells by immunocytochemistry (Bar: 100 μm) and Western blot. The ratio of LC3BII to GAPDH was quantified by using an imaging densitometer. (E) Ultrastructural changes of aliskiren on OGD-treated H9c2 cells by transmission electron microscopy. H9c2 cells appeared normal structure (C). Cell with OGD for 16 h showed necrosis (OGD-1) and apoptosis (OGD-2). Apoptotic cells displayed many vesicles and few autophagosomes in the cytoplasm (OGD-3). Many small vesicles were present in the cytoplasm (OGD + ALI-1). Abundant autophagsosomes (arrow) contained double membrane and cytoplasmic material such as mitochondria (OGD + ALI-2). Bar: 500 nm. Each of the experiments was repeated three times. The data are means ± SEM. GAPDH was used as an internal control. ∗P < 0.05 compared with the control, †P < 0.05 compared with OGD.
