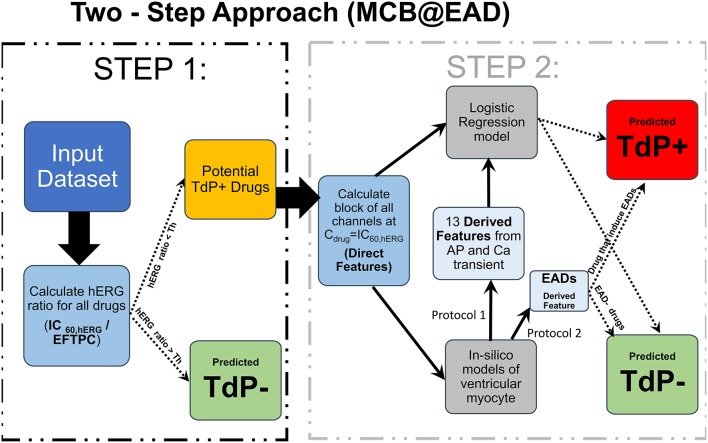
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the MCB@EAD two-step approach. In-vitro assay datasets are used to obtain the drug-induced blocks of multiple ion-channels at drug concentrations equal to IC60,hERG. hERG ratio () is used as the classification criteria in the first step. Drugs that do not result in 60% hERG block at concentrations well above their maximum EFTPC are classified as non-torsadogenic (TdP−). hERG ratio thresholds of 50, 100, 150, and 200 were tested, and the one that provides the best TdP risk discrimination was chosen for the particular datasets. The remaining drugs are considered to be potentially torsadogenic and analyzed in the second step. The drug-induced blocks of multiple ion-channels at 60% hERG block concentrations (direct features) are used as inputs to the logistic regression model for TdP risk classification or used to simulate drug-induced changes in action potential (AP) and calcium (Ca) transients using different protocols. The derived features are extracted from the AP and Ca transients. These derived features are then used to train the logistic-regression model for TdP risk classification or used directly (e.g., in case of EADs) to classify drugs to TdP+ and TdP− categories.