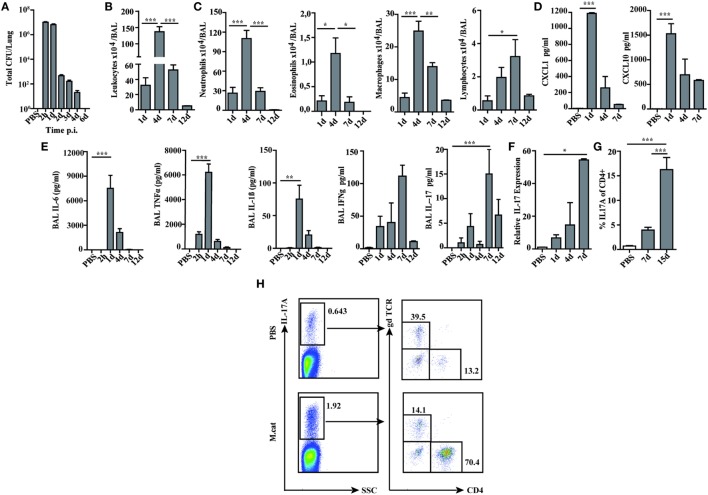
Figure 1.
Pulmonary immune response after intranasal M. catarrhalis infection. C57Bl/6 animals were infected (i.n.) with 2 × 108 CFU M. catarrhalis and BAL and lungs were harvested at indicated time points. (A) Bacterial CFU were determined in lung homogenates. (B) Total cell counts in BALF. (C) Differential cell counts in BALF. (D) CXCL1 and CXCL10 chemokines in BALF. (E) Cytokines in BALF. (F) Quantitative expression of IL-17 mRNA (qPCR) in lungs. (G) Frequency of IL-17A+CD4+ T cells in lungs. (H) Analysis of γδ T cells and CD4+ T cells secreting IL-17A at day 7 after PBS treatment or infection. n = 6 mice per group and two independent experiments were performed. ***P = 0.001, **P = 0.01, and *P = 0.05 (one-way ANOVA). BAL, bronchoaleveolar lavage; BALF, BAL fluid; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; ANOVA, analysis of variance.