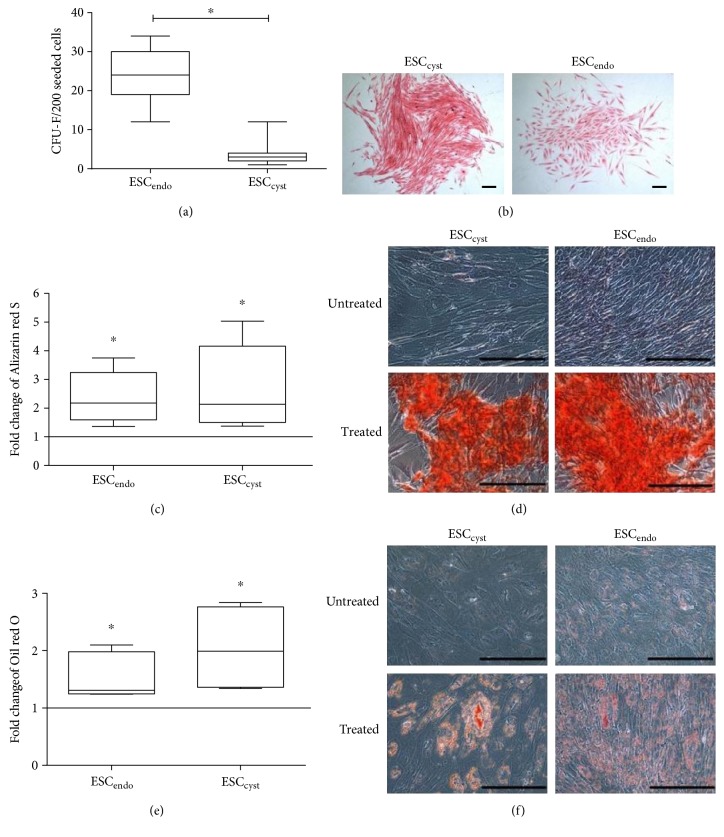
Figure 2.
Colony-forming unit fibroblasts for ESCendo and ESCcyst after they were cultured at clonal density for 21 days. Also, osteoblast differentiation for ESCendo and ESCcyst following 14–21 days culture in osteoblast differentiation growth medium and adipocyte differentiation for ESCendo and ESCcyst following 28-day culture in adipocyte differentiation growth medium are shown. The colony-forming efficiency (a) shows that ESCendo formed significantly more colonies than the ESCcyst (∗P < 0.05). Representative phase contrast images (b) at 4x magnification following Eosin staining of ESCendo and ESCcyst. Colonies with ≥50 cells were counted. Quantitation of the Alizarin red S dye (c) as a mean fold change relative to the untreated controls; both types of stromal cells significantly induced osteoblast differentiation (∗P < 0.05). Representative phase contrast images (d) at 20x magnification following Alizarin red S staining of the calcium salts. Quantitation of the Oil red O dye (e) as a mean fold change relative to the untreated controls; both types of stromal cells significantly induced adipocyte differentiation (∗P < 0.05). Representative phase contrast images (f) at 20x magnification following Oil red O staining of the lipid vacuoles. Nine independent experiments (n = 3 biological replicates) were carried out in triplicates for (a, b). Three to four independent experiments (n = 3 biological replicates) were carried out in duplicates for (c, d, e, f). Mean ± SD. Scale bars represent 50 μm at 4x magnification for (a,b) and 50 μm at 20x magnification for (c, d, e, f).