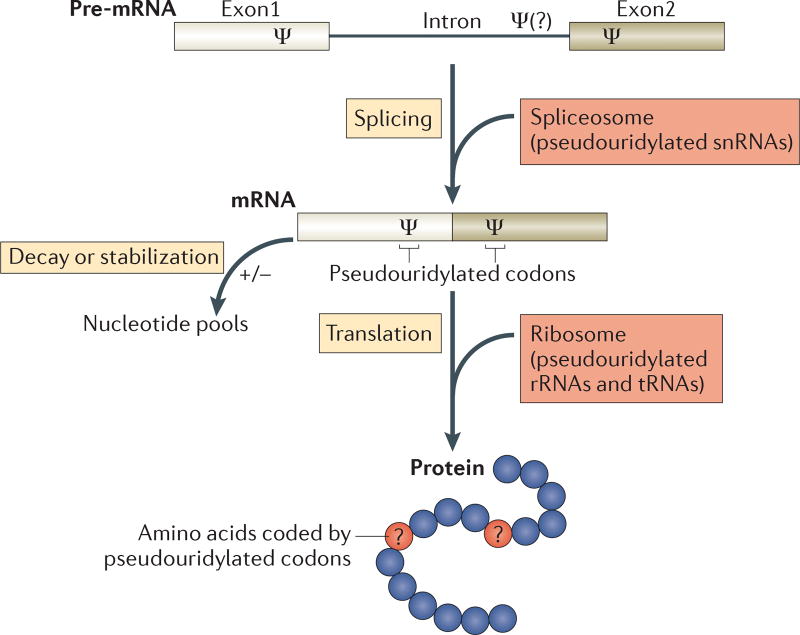
Figure 2. Possible roles of pseudouridines in gene regulation.
Pseudouridine (Ψ) nucleosides are introduced into pre-mRNAs at coding and non-coding exons and presumably also at introns. Given that they are present in pre-mRNAs and mRNAs, as well as in non-coding RNAs (such as spliceosomal small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and tRNAs) that are involved in every step in the pathway (splicing, translation and mRNA decay), pseudouridylation is likely to have a complex role in the regulation of gene expression. In fact, the functions of some pseudouridine residues in snRNAs, rRNAs and tRNAs have already been well characterized. In the schematic diagram of a protein (bottom), the blue circles represent amino acids coded by unmodified codons and the red circles (with question marks) represent amino acids coded by pseudouridylated codons. Although it is known that the pseudouridylation of nonsense (stop) codons can result in the suppression of translation termination, it is not clear whether pseudouridylation of sense codons will lead to changes in coding specificity.