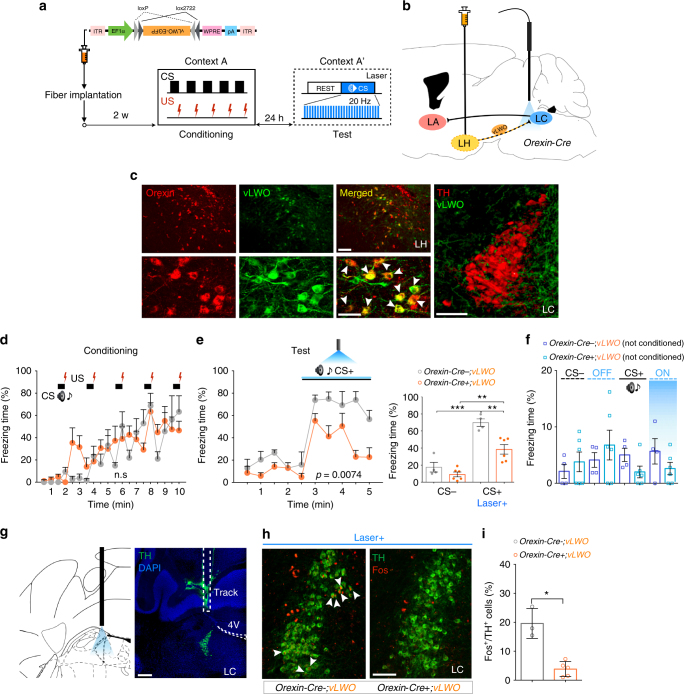
Fig. 4.
Optogenetic inhibition of orexinLH→LC decreased cued fear expression. a Experimental protocol. b Schematic representation showing sites for injection of AAV 10-FLEX-vLWO-EGFP and optic fiber. c Histological examination showing that orexin neurons express vLWO. Orexin is stained red, while vLWO-EGFP is stained green. Merged cells were shown by white arrow heads. Scale bars: upper panel, 100 μm; lower panel, 50 μm; right panel, 100 μm. Many vLWO-EGFP-positive fibers are observed in the LC. d, e After cued fear conditioning, acute optogenetic inhibition reduced freezing behavior against CS. f Laser stimulation or auditory CS itself had no effect in naive mice. g Track of an optic fiber implanted above the LC. Scale bar, 200 μm. h Images showing Fos+/TH+ cells (white arrow heads) in NALC neurons with or without optogenetic inhibition of the orexinLH→LC pathway. Scale bar, 100 μm. i Quantification of double-positive cells shown in the LC, suggesting that optogenetic inhibition of orexinLH fibers reduced the activity of NALC neurons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Values are mean ± SEM