FIGURE 5.
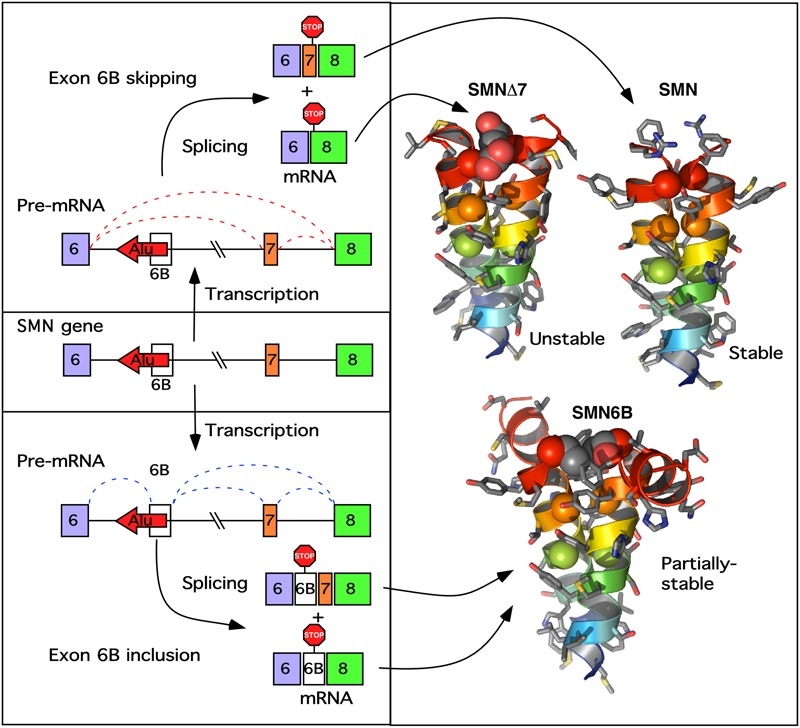
A model of exon 6B action. (Left) Describes the transcription of the SMN gene and pre-mRNA splicing producing either the 6B-skipped (upper) or 6B-included (lower mRNA). Exons are indicated as colored boxes, the Alu element from which exon 6B is derived is indicated as a red arrow, introns are shown as lines. Potential splicing events are shown as red (exon 6B-skipped) or blue (exon 6B-included) dotted lines. Locations of stop codons generated by each potential transcript are indicated. (Right) Shows the computationally predicted glycine zipper dimers formed by the YG boxes at the C termini of each of the SMN protein isoforms. Both SMNΔ7 and SMN6B have altered YG boxes resulting in an increase in the inter-helical distances of the coiled-coil interaction, potentially reducing oligomerization. In SMNΔ7 this results in an unstable degron (Cho and Dreyfuss, 2010), whereas in SMN6B the destabilization is less pronounced (Seo et al., 2016a).
