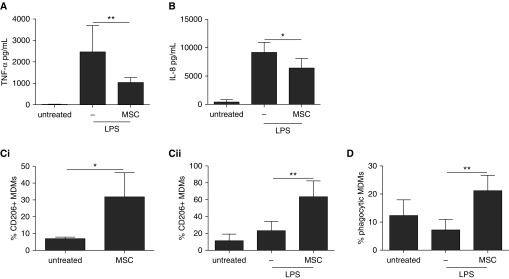
Figure 1.
Human mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) modulation of human monocyte–derived macrophage (MDM) phenotype and function. (A) MSCs in noncontact coculture reduced the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α by MDMs after 24 hours of LPS treatment. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni’s post hoc test was used (n = 5 per group). (B) IL-8 production by MDMs was reduced by MSC coculture after LPS treatment. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test was used (n = 4 per group). (C) MSC coculture increased the percentage of MDMs expressing CD206 on their surface in the (Ci) absence or (Cii) presence of LPS. Unpaired t test (n = 3 per group) and one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (n = 4 per group), respectively, were used. (D) MSCs increased the proportion of MDMs that had phagocytosed Escherichia coli pHrodo (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) dye-stained fluorescent bioparticles after LPS. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test was used (n = 5 per group). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.