Figure EV3. The chloroplast 4.5S ribosomal RNA .
-
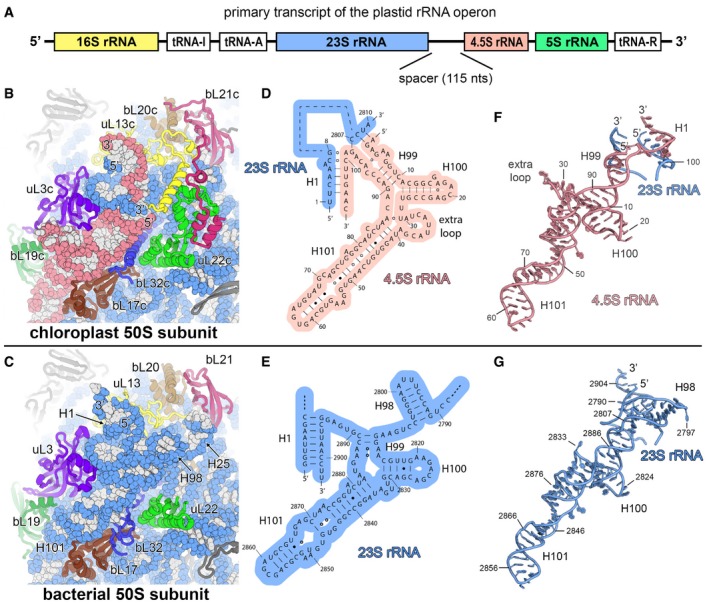
APrimary transcript of the chloroplast rRNA operon. The canonical sequences of ribosomal RNAs are indicated by coloured boxes. The 4.5S rRNA is separated from the 23S rRNA by a 115‐nucleotide RNA spacer.
-
B, CComparison of the chloroplast 50S subunit (B) with the bacterial 50S subunit (PDB 4YBB; Noeske et al, 2015) (C) indicating the structural rearrangement of the ribosomal proteins that interact with the 23S rRNA (blue) and the 4.5S rRNA (red).
-
D, ESecondary structure diagram of the chloroplast 4.5S rRNA (D) and the 3′ end of the bacterial 23S rRNA (E). The interactions of the 5′ and 3′ ends of the 4.5S rRNA with the 23S rRNA are shown. Watson–Crick base pairs are indicated by lines (‐), G•U base pairs by dots (•) and non‐standard base pairs by rings (○).
-
F, GModel of the chloroplast 4.5S rRNA (F) and the 3′ end of the bacterial 23S rRNA (G). The same nucleotides are shown in the models as represented in the secondary structure diagrams (D, E).
