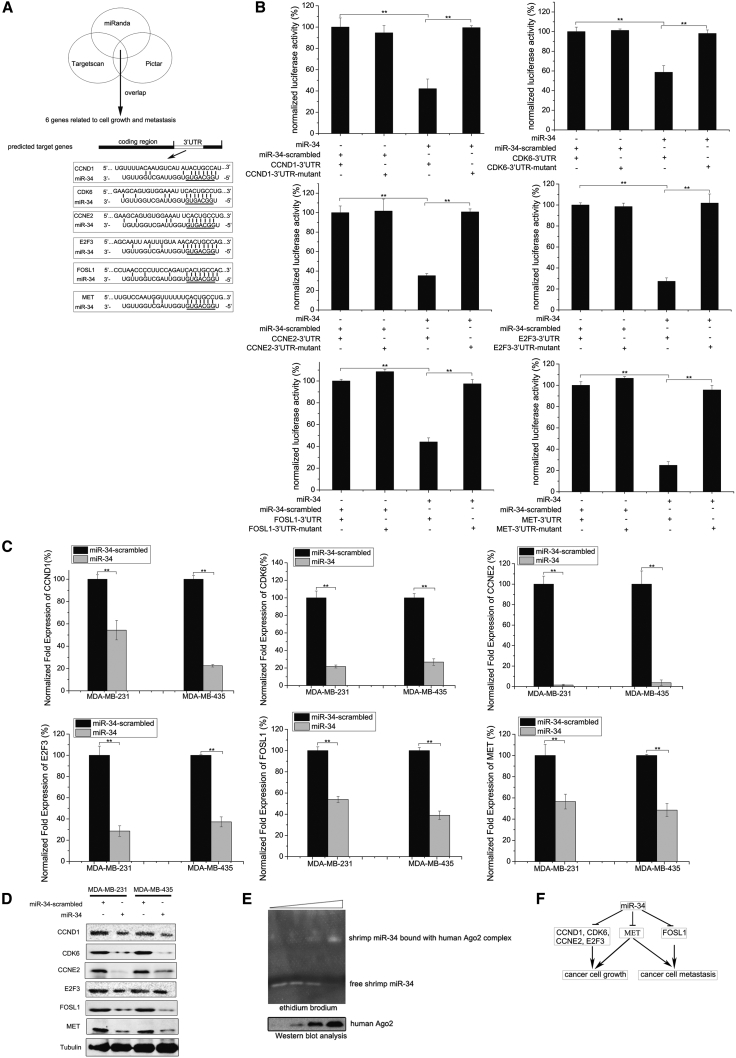
Figure 3.
The Mechanism of Shrimp miR-34 in Inhibiting Breast Cancer Progression
(A) The prediction of genes targeted by shrimp miR-34. The seed sequence of miR-34 is underlined. (B) The direct interaction between shrimp miR-34 and its target genes (i.e., CCND1, CDK6, CCNE2, E2F3, MET, or FOSL1) in breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231). Luciferase activity was normalized to the ratio of firefly and Renilla luciferase activities. (C) The effects of shrimp miR-34 expression on the expression of miR-34 target genes in breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435). (D) The influence of shrimp miR-34 expression on the expression of miR-34 target gene-encoding proteins in breast cancer cells. Protein levels were detected using western blot analysis. As a control, miR-34-scrambled was included in the transfection. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (E) The loading of shrimp miR-34 onto the human Ago2 complex. Shrimp miR-34 was incubated with the human Ago2 complex, followed by EMSA. Shrimp miR-34 was visualized by ethidium bromide staining (top). Human Ago2 protein was detected with western blot analysis (bottom). The wedge indicates the concentration gradient of human Ago2 complex. (F) A model for the role of miR-34-mediated cancer cell growth and metastasis. In all panels, statistically significant differences between treatments are represented with asterisks (error bar, SD; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01).