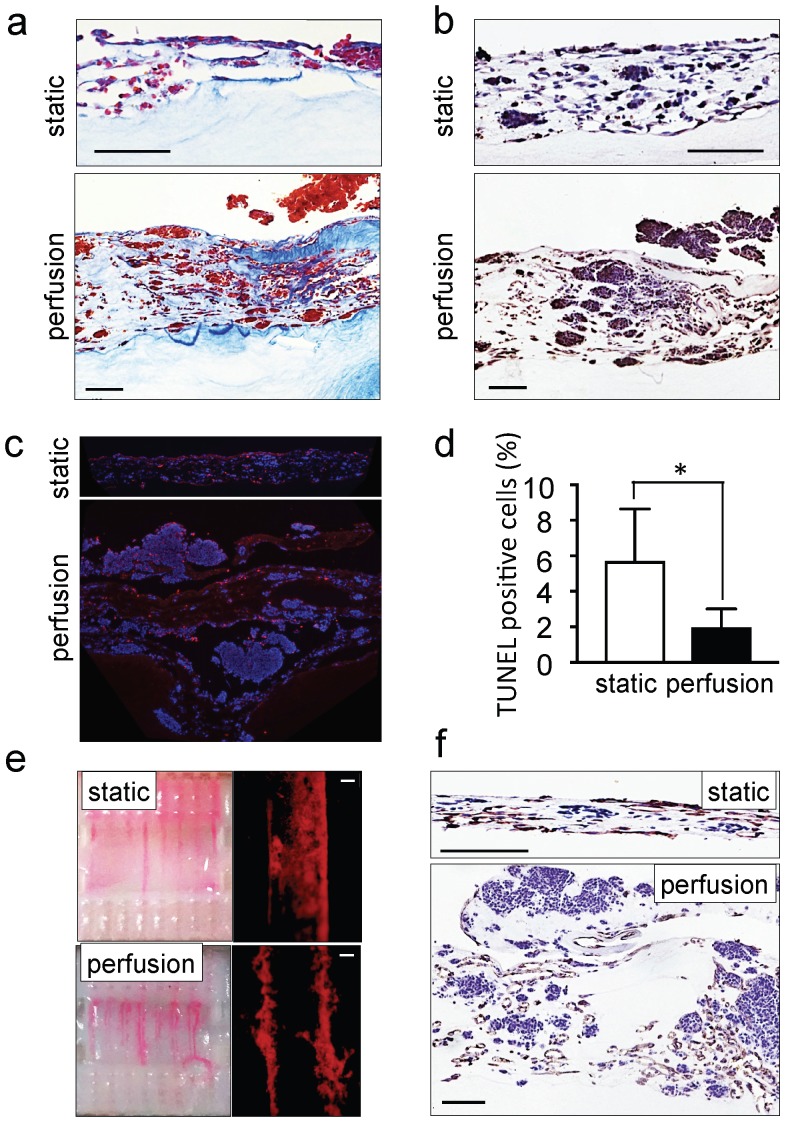
Figure 2.
Recapitulation of neuroblastoma vasculature in a perfusable tumor model. (a) AZAN staining and (b) ki67 staining of the tumor models under static or perfusion conditions, at day 4. Counterstaining with hematoxylin QS (blue) (Scale bar: 100 µm). (c) Fluorescence images showing apoptotic cells by TUNEL assay (red) under indicated conditions; nuclei are stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). (d) Percentages of apoptotic cells under static and perfusion conditions, determined by the TUNEL assay, and counted using the ImageJ software. Statistical significance was determined by the two-tailed Student's t test. ∗p < 0.05 (perfusion, n=6; static, n=3). (e) Demonstration of the formation of perfusable blood vessels by the presence of FluoSpheres Polystyrene Microspheres (in magenta) suspended in culture medium, in both the static and perfused tumor models, at day 4. Left: macroscopic analysis of the tumor model (top view). Right: microscopic analysis of perfusable channels (~300 µm in diameter) under static conditions and the formation of vessels (~50 µm in diameter) in the microchannels. Representative images are shown (n=3 per condition; scale bar: 100 µm). (f) Immunohistochemical staining for CD31 for the indicated conditions; Counterstaining with hematoxylin QS (blue), (scale bar: 100 µm).