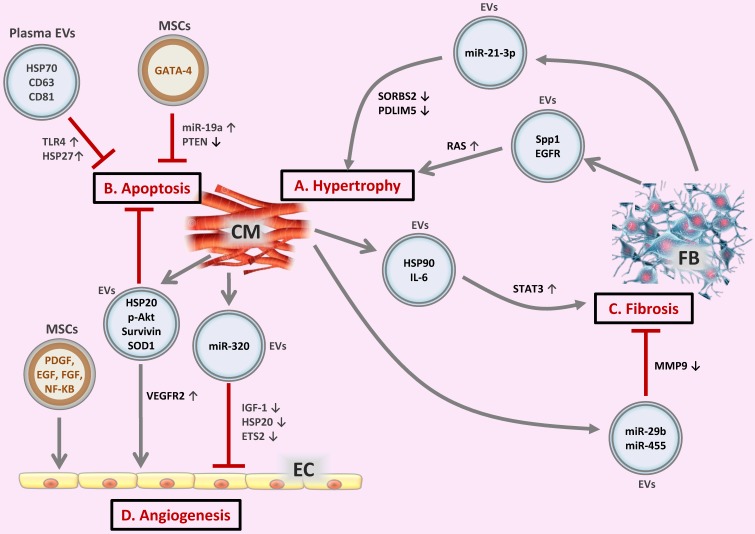
Figure 2.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the crosstalk of cardiac cells (A) FB-derived exosomes enriched with miR-21-3p or Spp1 and EGFR proteins are transferred to CMs, leading to CM hypertrophy. (B) EVs secreted from CMs or MSCs, as well as circulating EVs exert regulatory effects on CM apoptosis. (C) CM-derived exosomal HSP90 together with secreted IL-6 are able to activate STAT-3 signaling in cardiac FBs, leading to cardiac fibrosis; whereas CM-derived exosomes from exercised diabetic mice express high levels of miR-29b and miR-455, thus reducing cardiac fibrosis. (D) EVs secreted from CMs or MSCs are transferred to ECs, exerting pro- or anti-angiogenic activities. CM, cardiomyocyte; FB, fibroblast; EC, endothelial cell; Spp1, osteopontin 1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; RAS, renin angiotensin system; HSP, heat shock protein; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1.