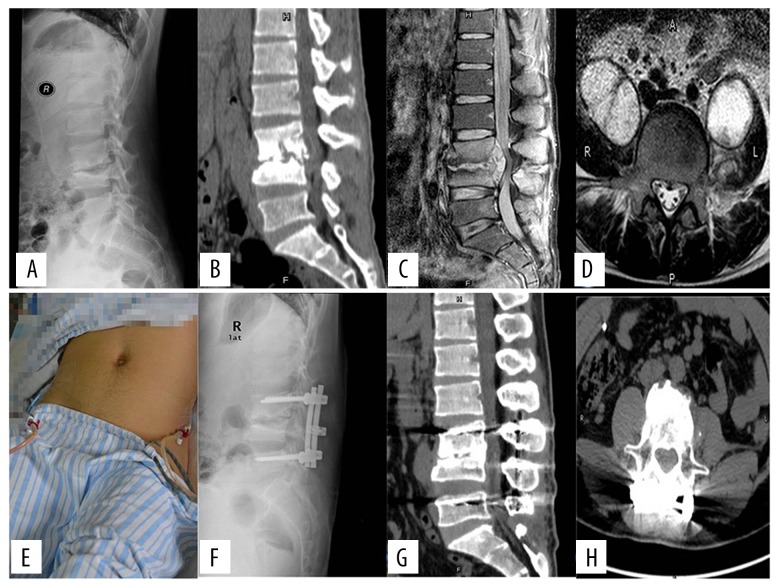
Figure 1.
Outcome of posterior lumbar debridement and spinal fusion, combined with a one-stage posterior (P) approach to percutaneous catheter drainage (PCD) for the treatment of lumbar tuberculosis with psoas abscess. A 42-year-old man underwent posterior percutaneous catheter drainage (P-PCD). Preoperative lateral X-radiograph (A) and sagittal computed tomography (CT) (B) showed spinal tuberculosis at L3–4. Preoperative sagittal magnetic resonance image (MRI) (C) and axial MRI (D) showed epidural abscess and bilateral psoas abscess: (E) PCD of bilateral abscess; (F) postoperative lateral X-radiograph; 18-month follow-up sagittal CT-can (G) and axial CT scan (H) showed that as bone fusion was achieved, the bilateral psoas abscess disappeared.