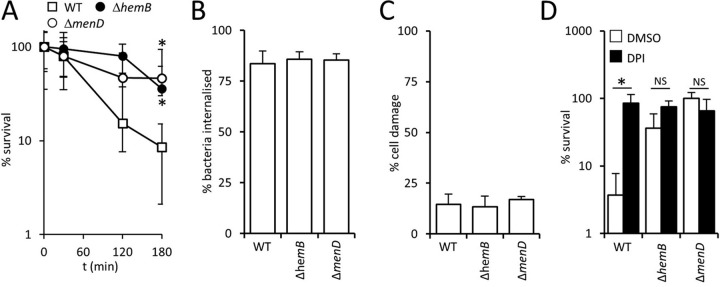
FIG 2.
SCVs survive the oxidative burst better than wild-type S. aureus. (A) Survival of wild-type S. aureus USA300 (WT) and ΔhemB and ΔmenD mutants in the presence of PMNs purified from human blood. (B) Percentages of S. aureus USA300 wild-type, ΔhemB, and ΔmenD bacteria internalized into phagocytic cells 2 h after inoculation into whole human blood. (C) Percentages of phagocytic cells that contained S. aureus strains, and had impaired membrane integrity, as determined using the Zombie Violet reagent after 6 h in whole human blood. (D) Survival of S. aureus USA300 wild-type, ΔhemB, and ΔmenD bacteria after 6 h in blood pretreated with the NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) or an identical volume of DMSO solvent alone (DMSO). In all cases, data are the mean of results of four independent experiments using blood from at least three different donors. Data in panel A were analyzed by a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Sidak's post hoc test. *, P < 0.01, compared with the wild type. For panels B to D, data were analyzed via a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. This revealed no significant differences between values in panels B and C. In panel D, an asterisk indicates a P of <0.01 and NS (nonsignificant) indicates a P of >0.05 when the indicated comparisons were made.