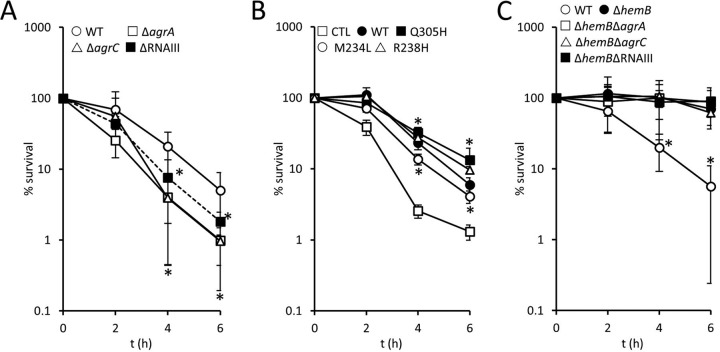
FIG 3.
Survival of wild-type but not SCV S. aureus is enhanced by Agr. (A) Survival of S. aureus USA300 wild-type (WT), ΔagrA, ΔagrC, and ΔRNAIII strains in whole human blood over 6 h. (B) Survival of S. aureus USA300 ΔagrC transformed with pCL55 (CTL), pCL55 containing the wild-type agrC gene (WT), and three mutated variants of agrC that result in Q305H, M234L, or R238H substitutions conferring a constitutively active phenotype. (C) Survival of S. aureus USA300 wild-type (WT), ΔhemB, ΔhemB ΔagrA, ΔhemB ΔagrC, and ΔhemB ΔRNAIII strains in whole human blood over 6 h. For all panels, data are the mean of results of four independent experiments using blood from at least three different donors. Data were analyzed by a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test to compare strains to the WT (A), CTL (B), or the ΔhemB mutant (C). *, P < 0.01. In panel A, all mutants were significantly more susceptible to immune defenses than the wild type at 4 and 6 h. In panel B, all strains expressing agrC (wild type or mutated) survived better than the ΔagrC mutant at the 4- and 6-h time points. In panel C, all ΔhemB mutants (with or without agr) survived equally well and significantly better than the wild type.