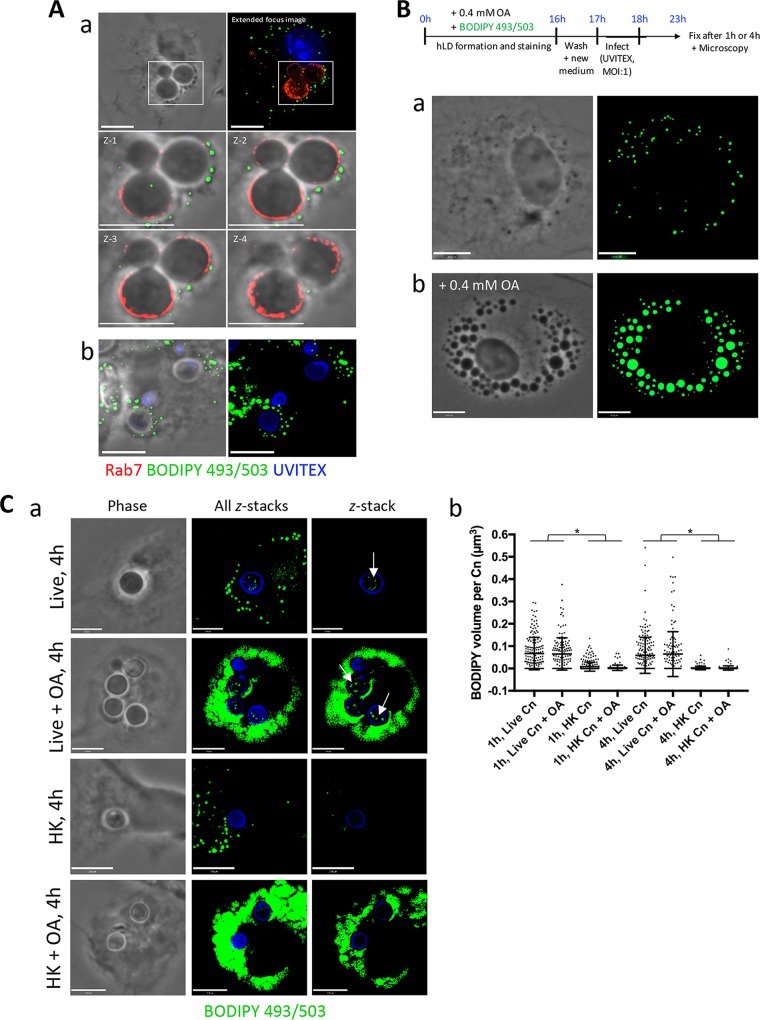
FIG 4.
C. neoformans scavenges OA or OA-derived lipids from its host, the macrophage. (A) Fluorescence microscopy of BMDM after a 2 h infection with C. neoformans, fixed and stained with antibodies for Rab7, Uvitex, and BODIPY 493/503 dye. The close apposition of host LD to the C. neoformans-containing phagosome is shown (a) and with 0.2 mM OA added (b). Scale bars, 7 μm. (B) Scavenging of OA or OA-neutral lipids by C. neoformans from the host BMDM. Schema outlining the experimental protocol is at the top. Briefly, BODIPY 493/503 was coadministered with 0.4 mM OA to BMDM overnight to induce the formation of fluorescent LD in the host cell. Following washes to remove BODIPY from the extracellular medium, live or HK C. neoformans infected the BMDM for 1 h or 4 h with (a) or without (b) 0.4 mM OA. In uninfected cells, the accumulation of the BODIPY dye into their LD is shown and increases with OA incubation. Scale bars, 7 μm. (C) Detection of LD in live C. neoformans following the uptake of FA stored in host LD. (a) BODIPY 493/503-positive foci within C. neoformans (arrows) were visible with no OA added and with 0.4 mM OA added during infection. Shown from left to right are phase-contrast images, extended-focus images (all z-stacks), and single z-stacks. No to little fluorescence was detected within HK fungi. (b) The fluorescence detected within individual fungi was quantified and graphed. Data are means ± SD of results of three separate assays, showing a significant increase in the presence of fluorescence within live C. neoformans (Cn) compared to that in HK C. neoformans. Results for all live versus HK samples are significant at a P of <0.0001 (indicated with an asterisk) by two-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple-comparison test. Scale bars, 6 μm.