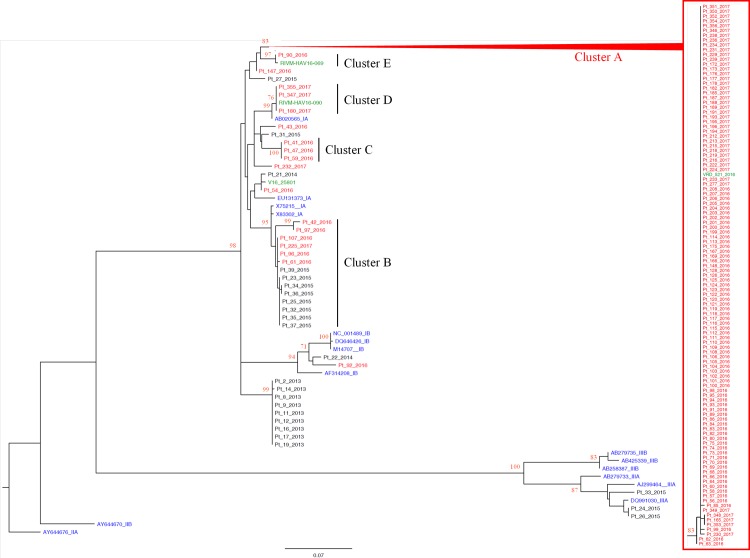
Fig 2. Phylogenetic analysis.
Phylogenetic tree, built with a total of 174 460nt-long sequences encompassing the VP1/2A junction region of HAV genome, based on the maximum-likelihood method with the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model + G. All the sequences obtained in 2016–2017 from Lazio region (N = 130, patient number, in red) are included. In addition, HAV sequences from Lazio cases referred to the Laboratory from 2013–2015 (N = 24, patient number, in black) are included. The tree also includes 16 reference sequences from GenBank (genotype IA: X75215; EU131373; AB020565; X83302; genotype IB: M14707; DQ646426; NC001489; AF314208; genotype IIA: AJ644676; genotype IIB: AY644670; genotype IIIA: AJ299464; DQ991030; AB279733; genotype IIIB: AB279735; AB425339; AB258387, in blue), and the 4 sequences (VRD_521_2016 and RIVM-HAV16-90, RIVM-HAV16-69 and V16_25801, in green) recently reported to be associated with epidemic clusters among MSM in other European countries (in blue). One genotype IIA sequence (AY644676) was used as the outgroup. The bar represents the genetic distance (substitution per nucleotide position). Bootstrap analysis with 1000 replicates was performed to assess the significance of the nodes; values greater than 80.