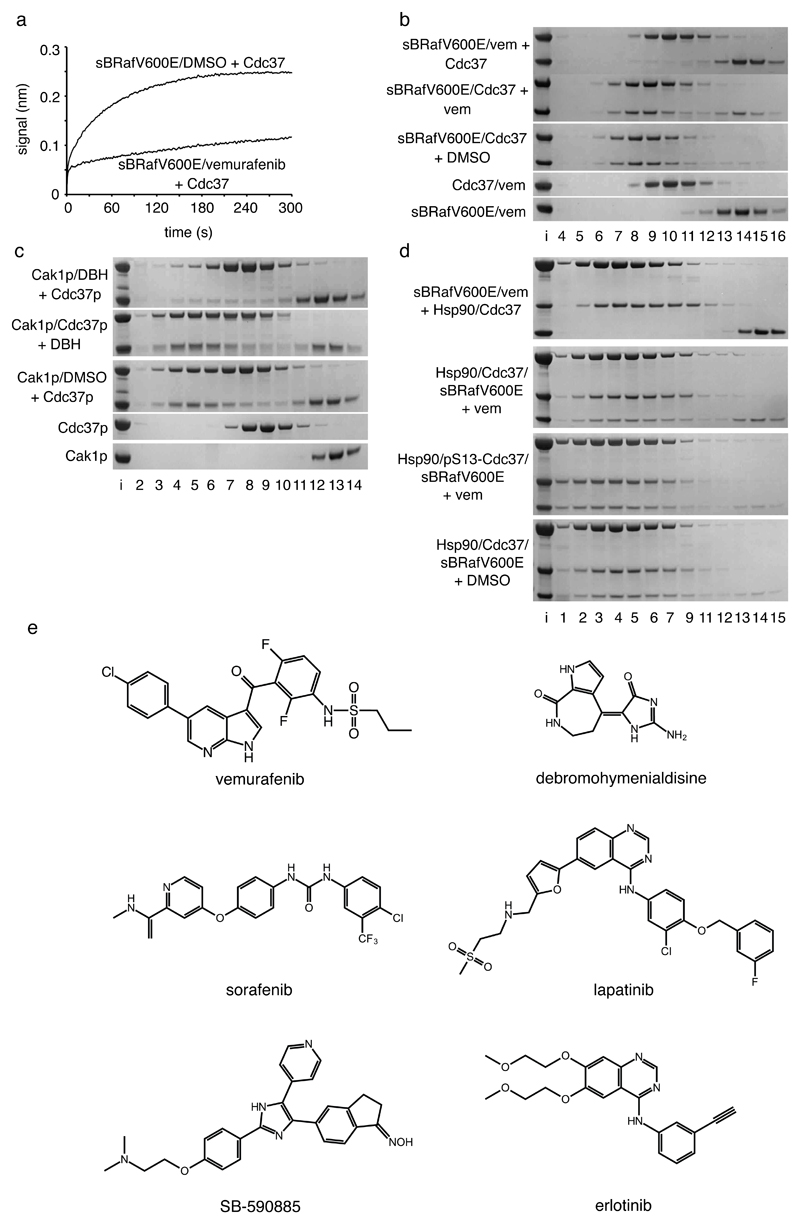
Figure 3. ATP-competitive inhibitors antagonise Cdc37 binding to kinases.
a. Octet Biosensor association curve for Cdc37 binding to immobilised His6-sBRafV600E in the absence or presence of vemurafenib. Binding is substantially inhibited by vemurafenib.
b. Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gels showing Superose 6 elution profiles (top to bottom): Cdc37 incubated with a pre-formed sBRafV600E-vemurafenib complex; sBRafV600E-Cdc37 complex incubated with vemurafenib; sBRafV600E-Cdc37 complex incubated with DMSO; Cdc37 incubated with vemurafenib; sBRafV600E incubated with vemurafenib. Vemurafenib prevents sBRafV600E recruitment to Cdc37 and is able to partially displace sBRafV600E from a pre-formed Cdc37-kinase complex.
c. As b, but with the budding yeast kinase Cak1p, budding yeast Cdc37p and the broad specificity kinase inhibitor debromohymenialdisine. DBH prevents Cak1p binding to Cdc37p, but is less able to disrupt a pre-formed Cak1p-Cdc37p complex.
d. As b – top to bottom: Hsp90β and Cdc37 incubated with a pre-formed sBRafV600E-vemurafenib complex; Hsp90β-Cdc37-sBRafV600E complex incubated with vemurafenib; Hsp90β-sBRafV600E complex with pSer13-Cdc37 incubated with vemurafenib; Hsp90β-Cdc37-sBRafV600E complex incubated with DMSO. Vemurafenib prevents the recruitment of sBRafV600E to the Hsp90β-Cdc37 complex and is able to partially displace sBRafV600E from the Hsp90β-Cdc37 complex. Ser13 phosphorylation stabilises the ternary complex towards vemurafenib relative to the unphosphorylated complex.
e. ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors that all antagonise Cdc37 binding to their target protein kinases, in vitro and/or in cells.