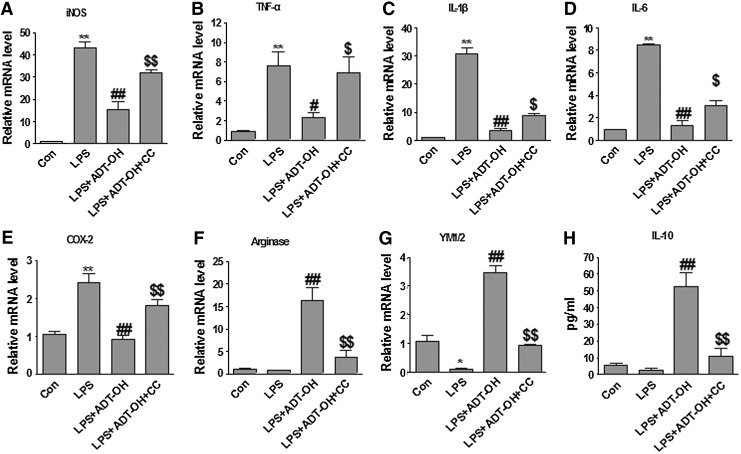
FIG. 4.
ADT-OH suppressed M1 signature gene expression while it increased M2 signature gene expression in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells, and both effects were attenuated by the AMPK inhibitor CC. (A–E) qPCR measurement of mRNA expression of M1 genes iNOS (n=3), TNF-α (n=6), IL-1β (n=4), IL-6 (n=3), and COX-2 (n=4) in BV2 cells at 6 h after LPS stimulation. ADT-OH suppressed LPS-evoked mRNA expression of iNOS, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2 in BV2 cells. ADT-OH suppression of LPS-evoked M1 gene expression was markedly attenuated by the AMPK inhibitor CC. (F, G) qPCR measurement of mRNA expression of the M2 genes arginase 1 and YM1/2 in BV2 cells at 6 h after LPS stimulation (n=3). ADT-OH enhanced mRNA expression of arginase 1 and YM1/2 in BV2 cells in the presence of LPS stimulation, which was markedly attenuated by the AMPK inhibitor CC. (H) ELISA measurement of IL-10 protein levels in media of BV2 cell cultures at 24 h after LPS stimulation (n=7). ADT-OH enhanced IL-10 production in the presence of LPS stimulation. ADT-OH-elevated IL-10 production was markedly attenuated by the AMPK inhibitor CC. *p<0.05 or **p<0.01, compared with control cells treated with vehicle (Con); #p<0.05 or ##p<0.01, compared with cells treated with LPS alone (LPS); and $p<0.05 or $$p<0.01, compared with BV2 cells treated with LPS plus ADT-OH (LPS+ADT-OH).